1. Article purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the BSEC peripheral and its main features,
- indicate the peripheral instances assignment at boot time and their assignment at runtime (including whether instances can be allocated to secure contexts),
- list the software frameworks and drivers managing the peripheral,
- explain how to configure the peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit | edit source]
The BSEC peripheral is used to control an OTP (one time programmable) fuse box, used for on-chip non-volatile storage for device configuration and security parameters.
Refer to the STM32 MPU reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software frameworks and drivers, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
3. Peripheral usage[edit | edit source]
This chapter is applicable in the scope of the OpenSTLinux BSP running on the Arm® Cortex®-A processor(s), and the STM32CubeMPU Package running on the Arm® Cortex®-M processor.
3.1. Boot time assignment[edit | edit source]
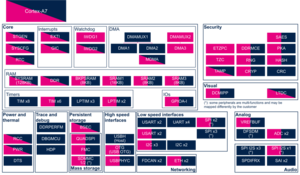
3.1.1. On STM32MP1 series[edit | edit source]
The BSEC is configured at boot time to set up platform security.
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Boot time allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (ROM code) |
Cortex-A7 secure (TF-A BL2) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (U-Boot) | |||
| Security | BSEC | BSEC | ✓ | ✓ | ☐ | |
3.1.2. On STM32MP2 series[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Boot time allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (ROM code) |
Cortex-A35 secure (TF-A BL2) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (U-Boot) | |||
| Security | BSEC | BSEC | ✓ | ✓ | ||
3.2. Runtime assignment[edit | edit source]
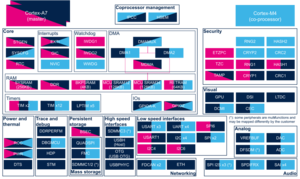
3.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) | |||
| Security | BSEC | BSEC | ✓ | ☐ | |
3.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Security | BSEC | BSEC | ✓ | ☐ | ⬚ | Cortex-M4 can read BSEC shadow register (BSEC_OTP_DATAx) to read a lower OTP value |
3.2.3. On STM32MP25x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 non-secure (STM32Cube) |
Cortex-M0+ (STM32Cube) | |||
| Security | BSEC | BSEC | ✓OP-TEE ✓TF-A BL31 |
|||||
4. Software frameworks and drivers[edit | edit source]
Below are listed the software frameworks and drivers managing the BSEC peripheral for the embedded software components listed in the above tables.
- Linux®: NVMEM framework
- OP-TEE: OP-TEE OTP overview
- TF-A BL2:
- TF-A BSEC2 driver for STM32MP1 series
- TF-A BSEC3 driver for STM32MP2 series
- U-Boot: U-Boot BSEC driver based on OP-TEE BSEC PTA
5. How to assign and configure the peripheral[edit | edit source]
The peripheral assignment can be done via the STM32CubeMX graphical tool (and manually completed if needed).
This tool also helps to configure the peripheral:
- partial device trees (pin control and clock tree) generation for the OpenSTLinux software components,
- HAL initialization code generation for the STM32CubeMPU Package.
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context in which the peripheral is assigned.
See also additional information in the BSEC device tree configuration article.