This article gives information about the Linux® RTC framework. The RTC framework is involved in precise time countdown.
1. Framework purpose[edit | edit source]
The RTC keeps the system time up-to-date and can wake up the system from the standby power mode at a programmed time.
A general presentation of the RTC framework is available in the Linux RTC documentation [1].
2. System overview[edit | edit source]
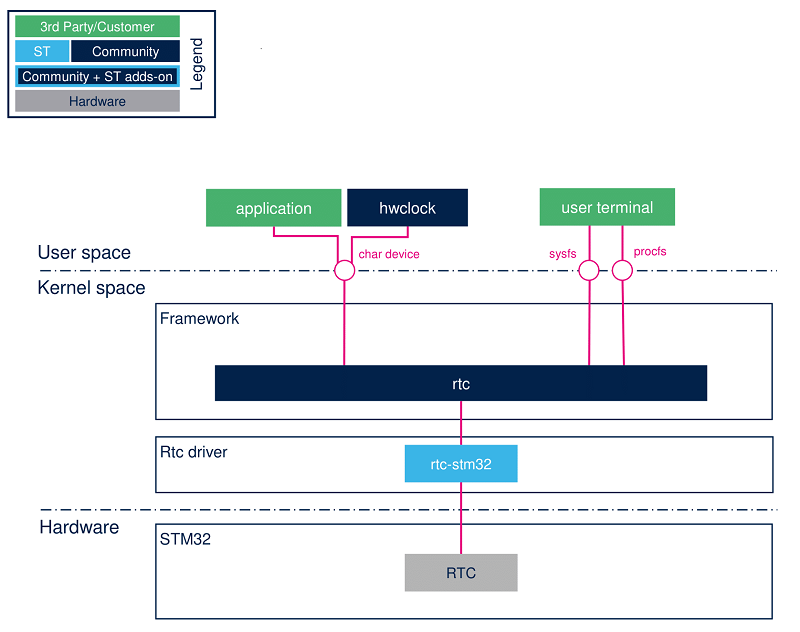
2.1. Component description[edit | edit source]
- RTC (hardware)
- RTC dedicated hardware block in STM32MPU product.
- rtc-stm32
- RTC ST driver.
- rtc
- Linux RTC framework, it provides API to RTC driver and interfaces to user.
- Sysfs interface
- Sysfs interface is accessible via /sys/class/rtc/rtcX/.
- Procfs interface
- Procfs interface is accessible via /proc/driver/rtc.
- Char device interface
- Device interface is accessible via /dev/rtcX.
- User application
- The user application can be a user built application or an community application such as hwclock.
2.2. API description[edit | edit source]
API is described in Linux RTC documentation [1].
3. Configuration[edit | edit source]
3.1. Kernel configuration[edit | edit source]
Activate rtc-stm32 driver in kernel configuration using the Linux Menuconfig tool: Menuconfig or how to configure kernel
Device drivers --->
-*- Real Time Clock --->
<*> STM32 RTC
3.2. Device tree configuration[edit | edit source]
Refer to the RTC device tree configuration.
4. How to use the framework[edit | edit source]
Refer to the How to use the RTC.
5. How to trace and debug the framework[edit | edit source]
5.1. How to trace[edit | edit source]
Dynamic debug traces can be added using the following command:
echo -n 'file rtc-stm32.c +p'>/sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
6. Source code location[edit | edit source]
- rtc-stm32: drivers/rtc/rtc-stm32.c
- api: include/linux/rtc.h
- framework:
- device-tree bindings constants: include/dt-bindings/rtc/rtc-stm32.h
7. References[edit | edit source]