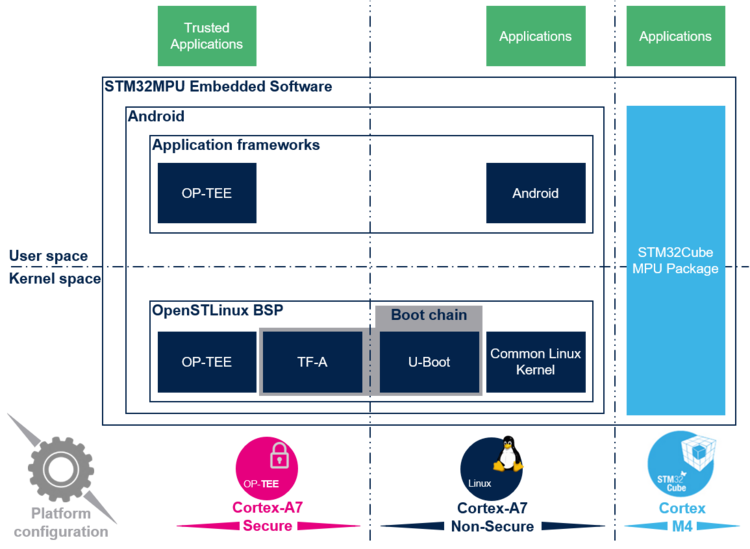
The diagram below shows STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution for Android main components:
- The OpenSTDroid distribution, running on the Arm® Cortex®-A, includes:
- The OpenSTLinux BSP with:
- The boot chain based on TF-A BL2 and U-Boot.
- The secure monitor based on TF-A BL31 running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in secure mode.
- The OP-TEE secure OS running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in secure mode.
- The Linux® kernel running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in non-secure mode.
- Application frameworks composed of middleware components relying on the BSP and providing a set of APIs:
- OP-TEE APIs to run Trusted Applications (TA) that allow manipulating secrets (information not visible from Linux® and from the STM32Cube MPU Package).
- Android APIs to run Applications that typically interact with the user via a display or a touchscreen.
- The OpenSTLinux BSP with:
- The STM32Cube MPU Package running on the Arm® Cortex®-M non secure mode: it is based on HAL drivers and middleware, like STM32 microcontrollers, completed with coprocessor management for interaction with the Cortex-A.
The figure below provides an overview of the STM32MPU Embedded Software architecture.
1. Open Source Software (OSS) philosophy[edit | edit source]
The Open source software source code is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to study, change and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose[1].
STMicroelectronics maximizes the using of open source software and contributes to those communities. Notice that, due to the software review life cycle, it can take some time before getting all developments accepted in the communities, so STMicroelectronics can also temporarily provide some source code on github[2], until it is merged in the targeted repository.
2. References[edit | edit source]