This article gives information about the OTP framework in OP-TEE and the associated interfaces.
1. Framework purpose[edit | edit source]
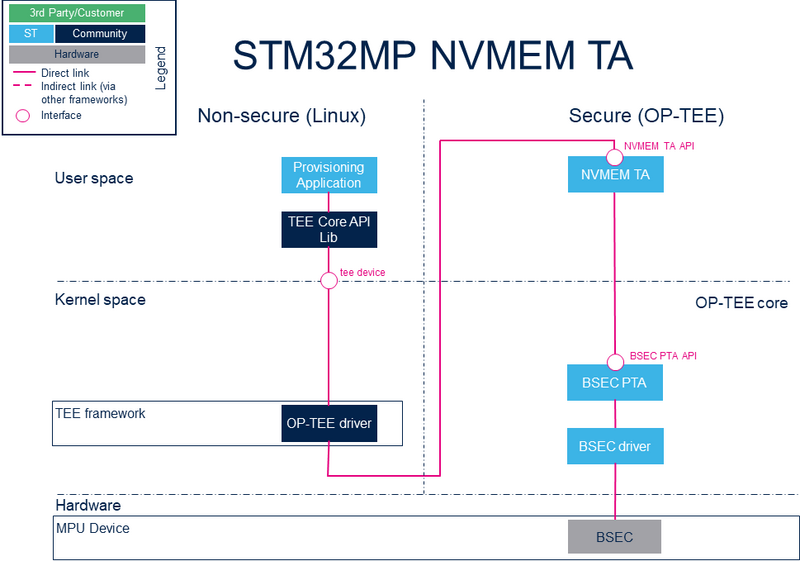
The two OP-TEE trusted applications (TA), STM32MP BSEC and STM32MP NVMEM, provide a generic interface for the device nonvolatile OTP (one-time programmable) fuses.
These two TAs offer interfaces to read and/or write OTP data and status at other TAs in a secure world and in nonsecure applications.
2. System overview[edit | edit source]
- OP-TEE BSEC PTA
- OP-TEE NVMEM TA
2.1. Component description[edit | edit source]
- Nonsecure world (Linux):
- NVMEM framework (kernel space) : The NVMEM framework in Linux® kernel provides a sysfs interface and an NVMEM API.
- NVMEM drivers (kernel space): Provider drivers such as BSEC Linux® driver that exposes OTP data to the core.
- TEE Core API Lib (User Space): Library called by the client application to access to the kernel space.
- TEE framework (kernel space): The TEE framework provides TEE client API to communicate with secure services, as the services provided by the OP-TEE Linux® driver.
- OP-TEE driver (Kernel Space): Generic driver that sends messages to the OP-TEE OS.
- Secure world: the OP-TEE secure OS runs on the Cortex-A in secure mode and exposes secure service with trusted applications (TA)
- STM32MP NVMEM TA (User mode): early TA that exposes the NVMEM specific services for provisioning by nonsecure world.
- STM32MP BSEC PTA (OP-TEE core): pseudo TA (PTA) that exposes the BSEC specific services for OTP acccess by nonsecure world or to other TAs.
- BSEC driver (OP-TEE core): core/drivers/stm32_bsec.c
- Hardware: access to hardware specific peripherals
2.2. API description[edit | edit source]
The OTP interface is provided by two trusted applications (TA) in OP-TEE, accessible from the normal world with the GlobalPlatform TEE Client API:
- STM32MP BSEC PTA: used to export OTP to other TA or to normal world (individual access)
- STM32MP NVMEM TA: used to export OTP to the STM32cubeProgrammer (global access for provisioning)
3. Configuration[edit | edit source]
3.1. OP-TEE_OS configuration[edit | edit source]
Activate STM32MP BSEC PTA in OP-TEE configuration core/arch/arm/plat-stm32mp1/conf.mk :
CFG_BSEC_PTA ?= y
Activate BSEC driver write support in OP-TEE configuration core/arch/arm/plat-stm32mp1/conf.mk :
CFG_STM32_BSEC_WRITE ?= y
In ecosystem release ≤ v4.1.0 ![]() , this configuration is activated on OP-TEE debug release with:
, this configuration is activated on OP-TEE debug release with:
CFG_STM32_BSEC_WRITE ?= $(CFG_TEE_CORE_DEBUG)
Activate STM32MP NVMEM TA in OP-TEE configuration core/arch/arm/plat-stm32mp1/conf.mk :
CFG_TA_STM32MP_NVMEM ?= y
3.2. Device tree configuration[edit | edit source]
Detailed DT configuration for STM32 internal peripherals:
4. How to use the OP-TEE OTP interfaces[edit | edit source]
The access to a trusted application (TA) is done with TEE client API architecture/globalplatform_api.html#tee-client-api.
4.1. STM32MP BSEC PTA[edit | edit source]
The STM32MP BSEC PTA interface runs at TEE kernel level and provides access to OTP data and status: lock and error. (core/arch/arm/plat-stm32mp1/bsec_pta.c )
This interface is used by trusted applications (TAs) in a secure environment to access all available OTP that are not masked by hardware.
See the example in the STM32MP NVMEM TA: ta/stm32mp_nvmem/ta_stm32mp_nvmem.c . This access is only allowed for an open device (checked during open session), but there is no access restriction for other trusted applications.
This interface is also used by nonsecure world BSEC driver to access an unsecured OTP:
- Linux: drivers/nvmem/stm32-romem.c
- U-Boot: arch/arm/mach-stm32mp/bsec.c
Only the lower OTP words are by default accessible by the nonsecure world (TEE_LOGIN_REE_KERNEL). The software needs to manage exceptions to allow some upper OTPs to be accessed by the nonsecure world as described in BSEC_device_tree_configuration. When an OTP is not accessible, the returned value is 0x0.
4.2. STM32MP NVMEM TA[edit | edit source]
The STM32MP NVMEM early TA interface runs in a secure user environment and allows accessing a secure nonvolatile memory (NVMEM), by exchanging buffer with provisioning application and with STM32CubeProgrammer tools (ta/stm32mp_nvmem/ta_stm32mp_nvmem.c ).
See example in U-Boot: arch/arm/mach-stm32mp/cmd_stm32prog/stm32prog.c .
5. References[edit | edit source]
Please refer to the following links for additional information: