1. Discontinuous PWM (DPWM) overview
DPWM feature allows the users to reduce the switching losses with an additional modulation technique according to their application.
This new approach is added to the current default 3-phase modulation.
It is deployed in all supported configurations:
- 3-Shunt
- 1-Shunt
- ICS
- with sensor or sensorless.
DPWM mode is available to the overall MCU families supported by STM32 MC SDK5.x
Target market:
- Home appliances / High voltage applications: Air-conditioner fan, Air-conditioner compressor, Refrigerator compressor
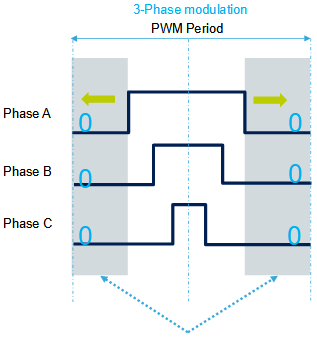
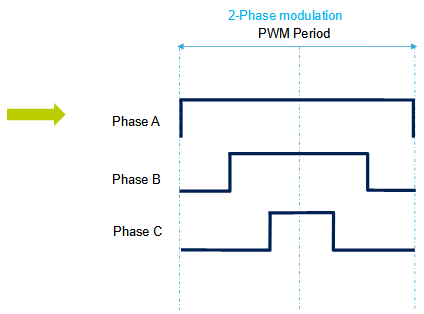
2. DPWM / Two-phase description
By suppressing (0,0,0) state, two switches per cycle can be removed (here named with low side – usually high side):
Duty_A is enlarged of PWM_period – Duty_A to cover the whole PWM period.
In this case, as (1,1,1) state is enlarged of Duty_A:
- Duty_B = Duty_B + Duty_A
- Duty_C = Duty_C + Duty_A
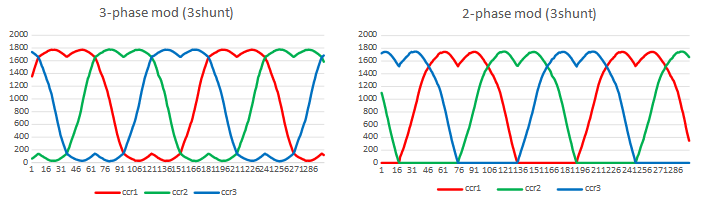
3. Two-phase versus three-phase modulation
CCR1,CCR2,CCR3 – applied PWM duty on U,V,W
4. DPWM activation via STM32 MC Workbench setting
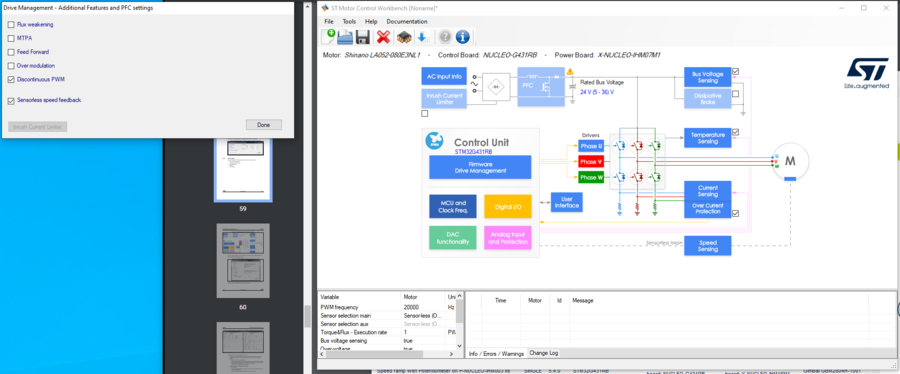
To enable the DPWM mode, select "Discontinuous PWM" parameter settings in “Firmware Drive Management / Additional Features” as shown below.
5. DPWM firmware changes
When a project is generated with the DPWM, the activation of 2-phase modulation is effective at the startup stage, just after the calibration.
DPWM is enabled all-time in the 3-Shunt case, while it is not true in 1-Shunt.
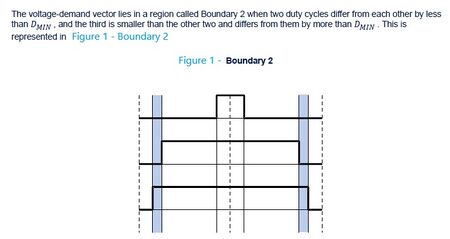
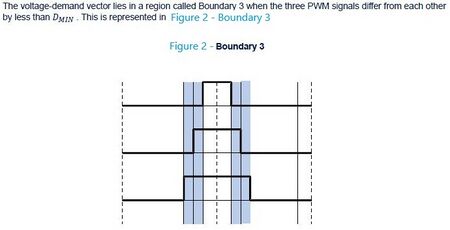
In the 1-Shunt case, since the A and B stages are used for current sensing in boundary 2 or 3, it is not possible in this specific situation to work in 2-phase SVPWM. The workaround consists to automatically switch in 3-phase during these transition stages.
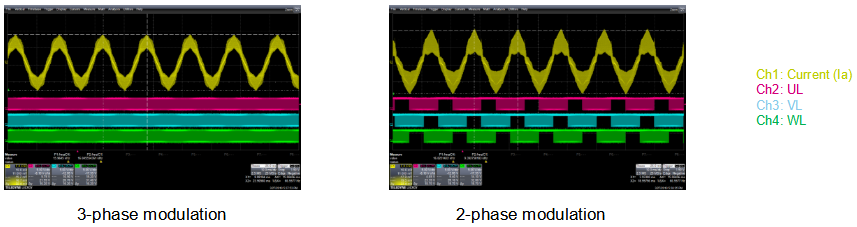
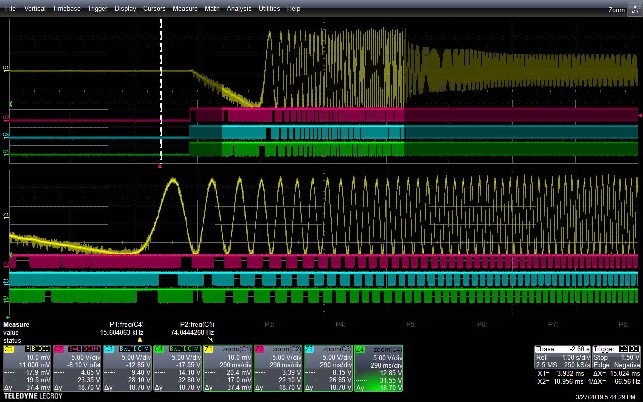
5.1. Example 1: two-phase versus three-phase modulation
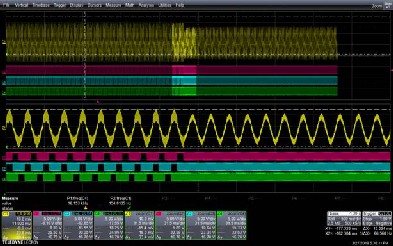
Dynamically moving from 3-phase modulation to 2-phase modulation:
Legend: Ch1: Current (Ia) Ch2: UL Ch3: VL Ch4: WL
5.2. Example 2: two-phase modulation: Startup in 3-Shunt mode
Here is a snapshot capture of the startup phase in DPWM mode.