Target description
This tutorial aims to help you to:
- Use the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield that includes a TCPP03-M20 protection circuit and provides a USB Type-C® connector.
- Create a USB PD dual-role application with the NUCLEO-G071RB board and the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield by using STM32CubeIDE software.
Prerequisites
- Computer with Windows 7 (or higher)
Hardware
- NUCLEO-G071RB (tested on rev C)[1]
- X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield[2]
- USB PD Sink device (to test our USB source device, it can be the sink created in this wiki article or a USB Type-C® mobile phone or device.)
- USB PD source device (to test our USB source device, it can be the sink created in this wiki article or a USB Type-C® mobile phone or device.)
- USB cable Type-A to Micro-B
- USB Type-C® to Type-C® cable
Software
Literature
- UM2324 NUCLEO-G071RB User Manual
- UM2891 X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 User Manual
 How to build an USBPD Dual-Role application using the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack
How to build an USBPD Dual-Role application using the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack
Create a USB PD dual-role device
![]() Total 60min
Total 60min
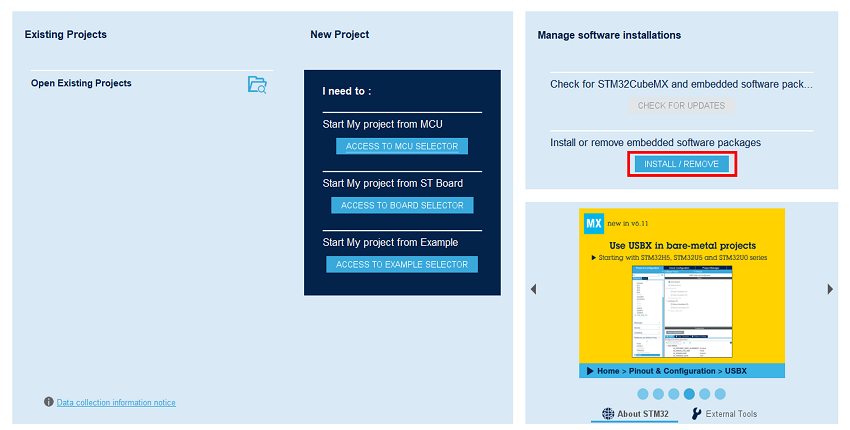
1. Software pack installation
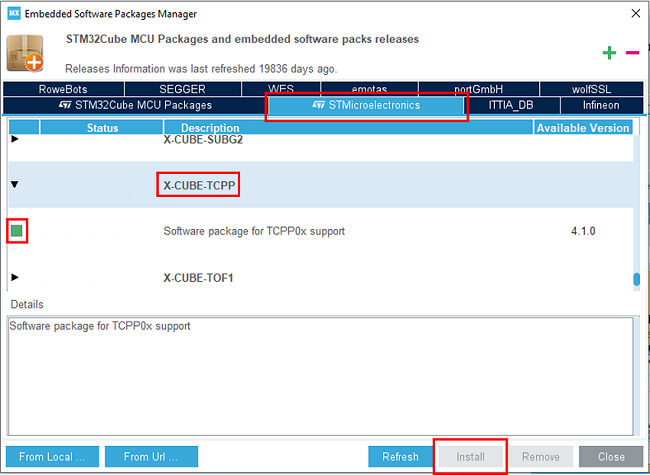
Open STM32CubeMX, in the software pack area, click on the install/remove button.
Then select the STMicroelectronics tab, scroll down to the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack, and click on the install button if it is not already installed.
2. Creating the project
![]() 5min
5min
IN STM32CubeMX, create a new STM32 project. As a target selection, choose the NUCLEO-G071RB from the board selector tab.
Click start project, then in the file menu, create a new folder at your project's name, and click save.
3. Configuring the system
At this point, your project is created and in the next steps, we will configure the peripherals and options needed for the project.
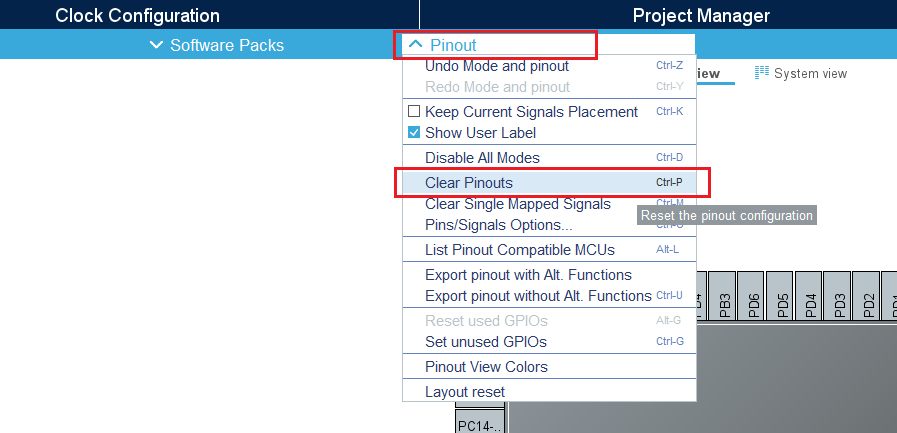
3.1. Clear the pinout
To start from a blank configuration, click on the pinout menu and select clear pinouts. This resets the pinouts in the pinout view.
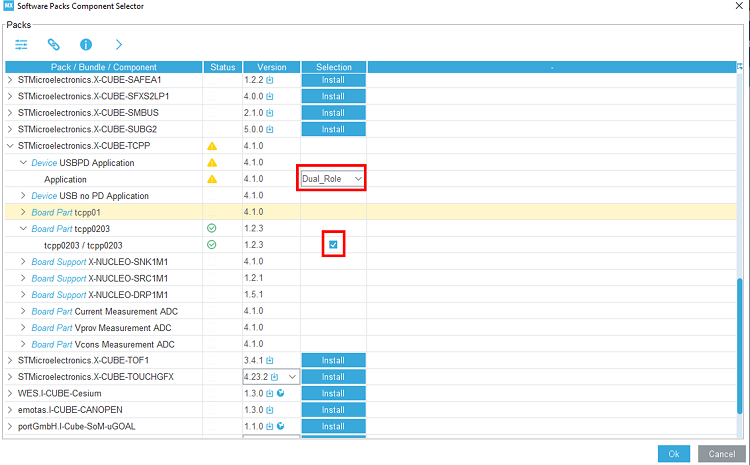
3.2. Select the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack
Click on the software pack menu.
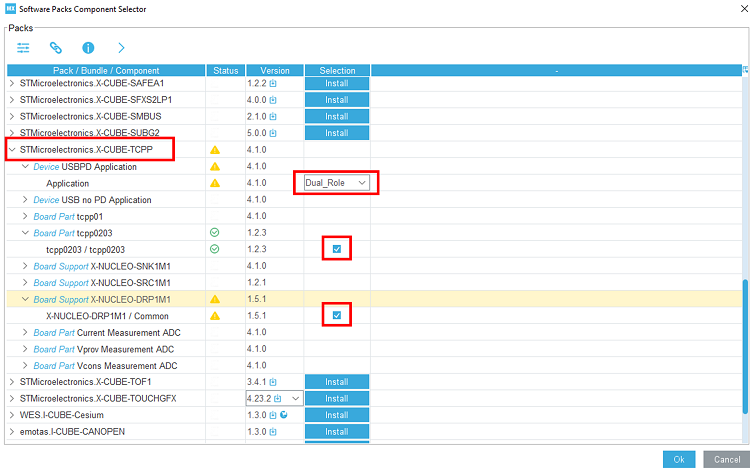
Select the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack and enable its source application, the tcpp0203 Board part and the X-NUCLEO-SRC1M1 Board support.
3.3. Configure UCPD peripheral
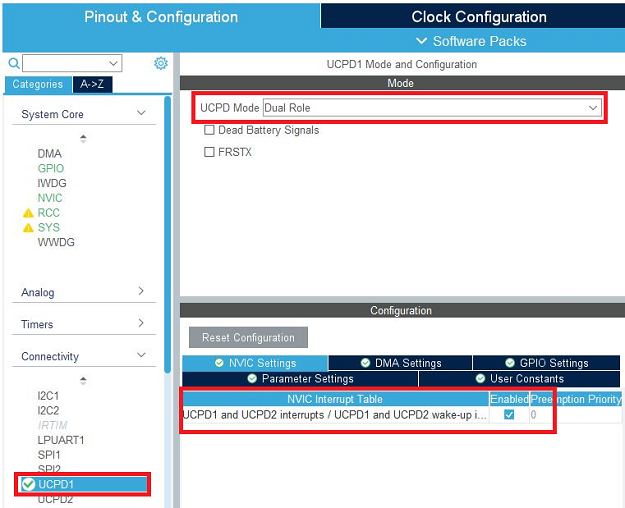
In the connectivity tab, select the UCPD1 peripheral and enable it in dual-role mode. Under the NVIC settings tab, enable UCPD global interrupts.
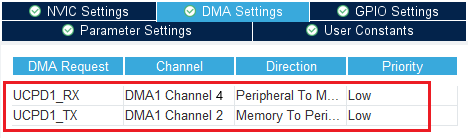
Under the DMA settings tab, add UCPD1_RX and UCPD1_TX DMA requests. Select DMA1 channel 4 for RX and DMA1 channel 2 for TX.
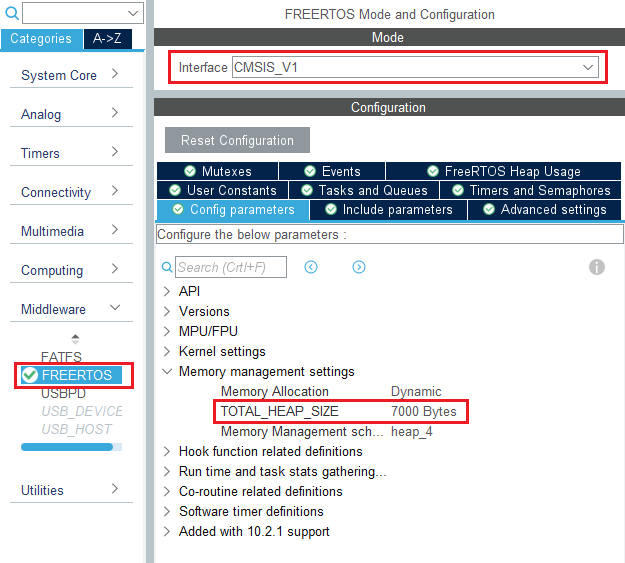
3.4. Configure FreeRTOS middleware
In the middleware section, enable FreeRTOS with the CMSIS_V1 interface. Under the config parameters tab, change "TOTAL_HEAP_SIZE" to 7000 bytes.
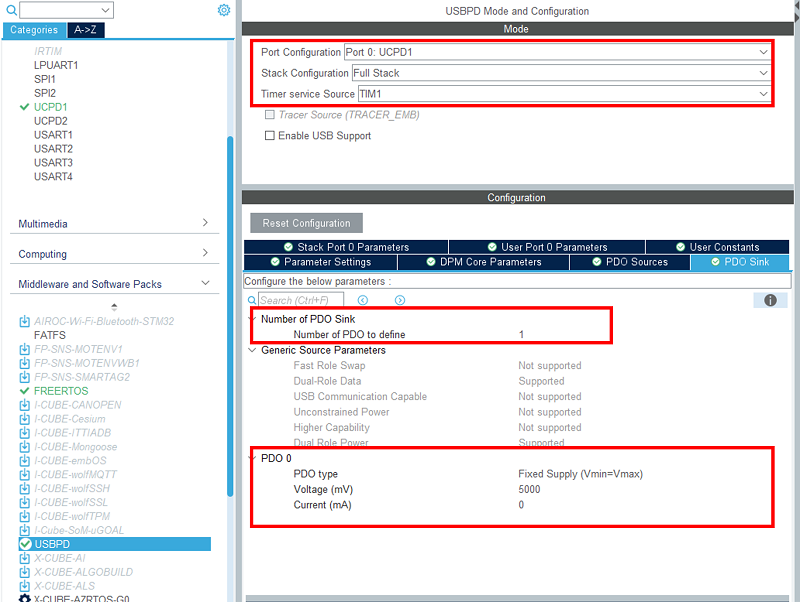
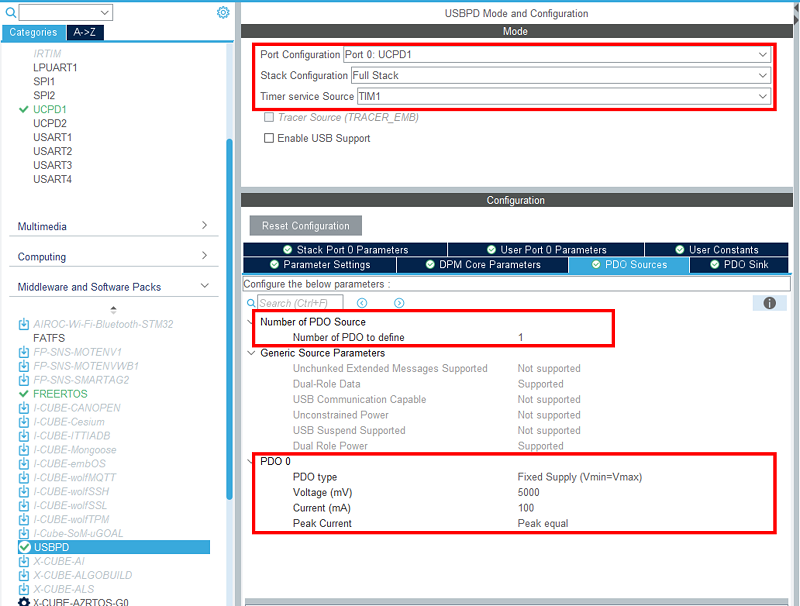
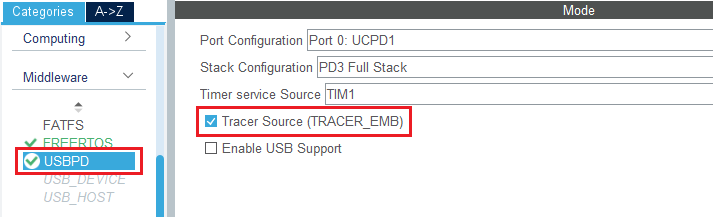
3.5. Configure USB PD middleware
In the middleware section, enable USBPD with the following configuration:
- Port configuration: Port 0: UCPD1
- Stack configuration: PD3 full stack
- Timer service source: TIM1
Under the PDO Sink tab, verify the following configuration:
- Number of sink PDOs for port 0: 1
- Port 0 sink PDO 1 5V
- Number of source PDOs for port 0: 1
- Port 0 source PDO 1 5V 100mA
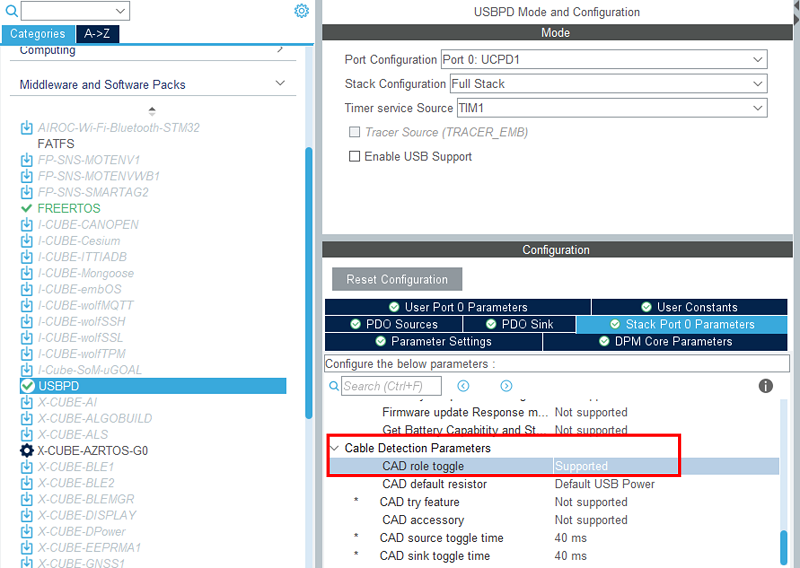
In the stack port 0 parameters section, enable the CAD role toggle: CAD role toggle: Supported
3.6. Configure ADC peripheral
For the power delivery stack to work, VBUS needs to be monitored. To do it, an ADC needs to be configured to measure the VBUS voltage and current.
As we are going to use the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 BSP, the ADC configuration does not need to be done in CubeMX.
As we need the ADC HAL drivers for it to work properly, we still need to configure the ADC in CubeMX for it to include the driver files, but the actual configuration and init function will not be called in our project.
In the analog section, enable ADC1 peripheral channel 0. Leave the configuration as default, as the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 BSP reconfigures it.
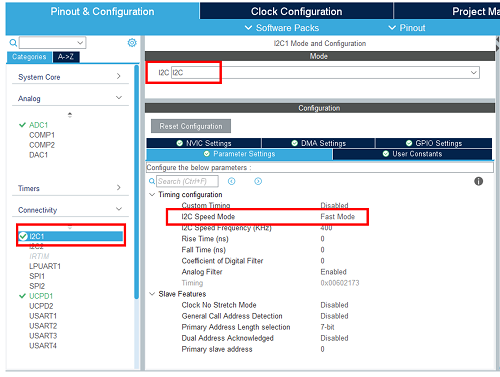
3.7. Configure I2C peripheral
As the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield includes a TCPP03-M20 that communicates via I2C, we need to enable the I2C peripheral in our project.
In the connectivity section, enable I2C1 peripheral, in I2C mode. Leave the configuration as default, as the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 BSP reconfigures it.
Note: We need to enable the I2C1 peripheral in the CubeMX view for code generation to include the I2C drivers as we do for the ADC.
3.8. Enable the software pack
In the middleware and software pack category, select the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack. Enable the 'source' application, the 'tcpp0203' Board part and the 'X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1' Board support.
3.9. Configure clocks
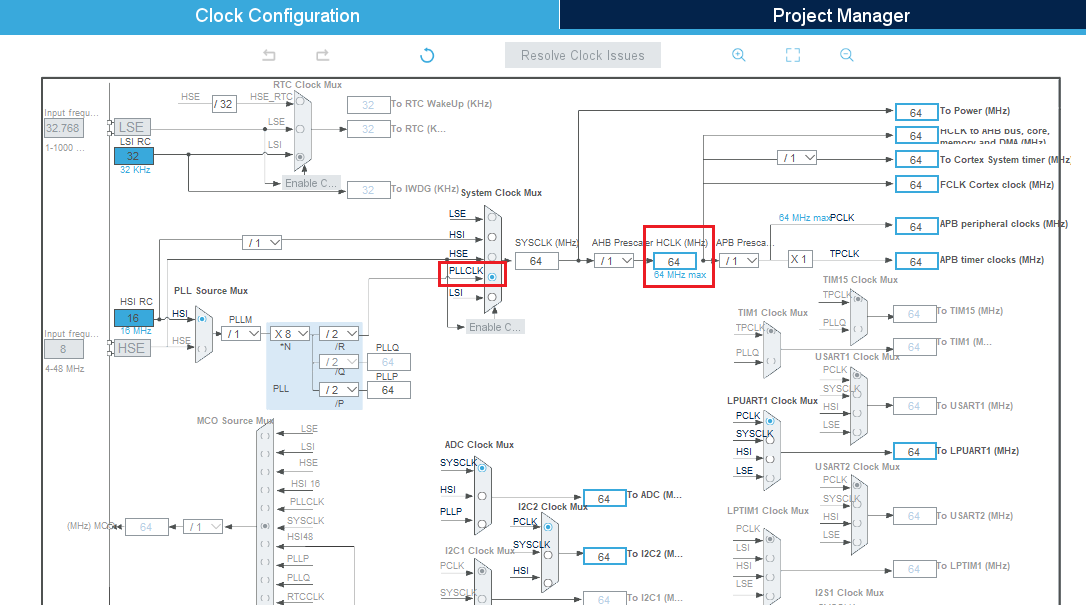
Under the clock configuration main tab, change the system clock mux to PLLCLK. It sets the HCLK clock to 64 MHz.
3.10. [OPTIONAL] Configure tracer for debug
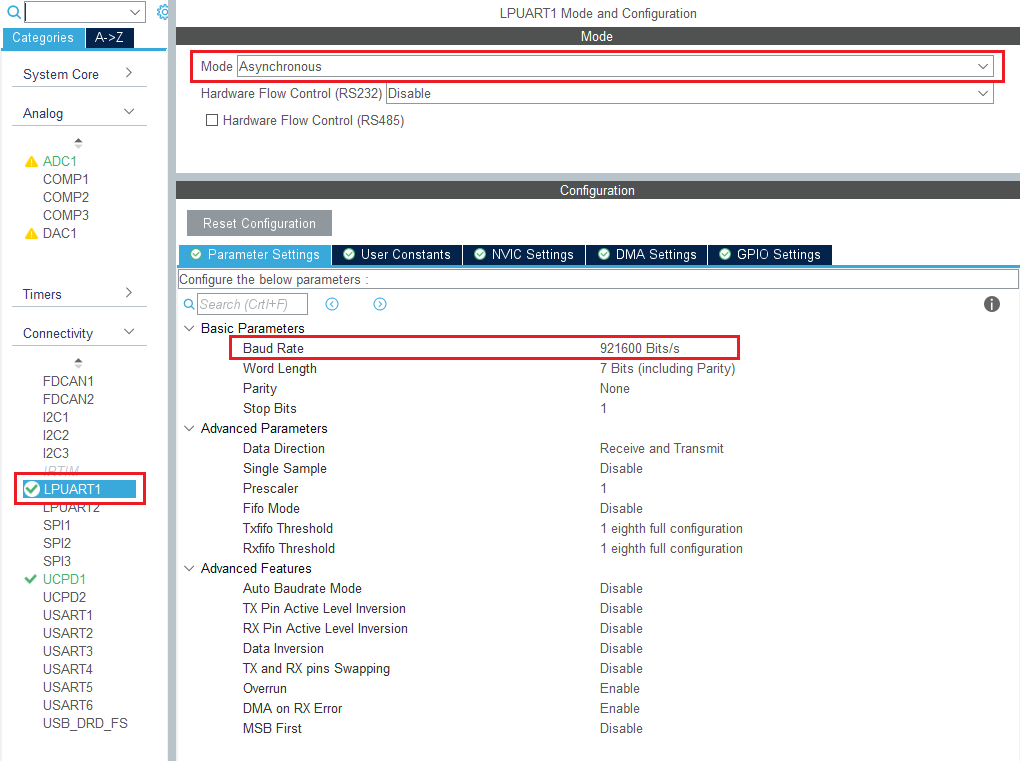
3.10.1. Configure LPUART
On the STM32G0 Nucleo-64 board, the virtual COM port connected to the STLINK is the LPUART1.
In the connectivity section, enable LPUART1 in asynchronous mode, and baud rate 921600 bauds. Leave the rest as default.
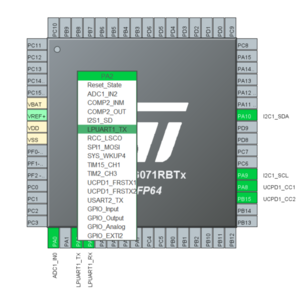
In the pinout view, left-click PA2 and PA3 to remap them to LPUART1_TX and LPUART1_RX.
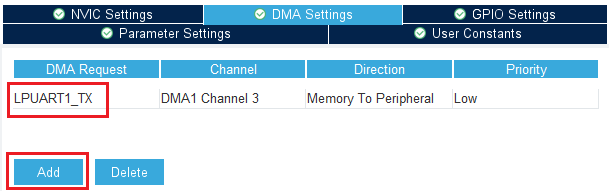
Under the DMA configuration tab, add a request for LPUART1_TX. Use DMA1 channel 3.
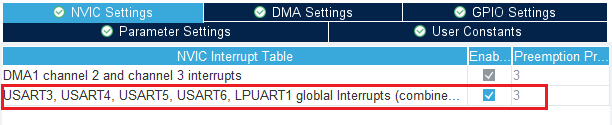
Finally, under the NVIC settings tab, enable LPUART1 global interrupts.
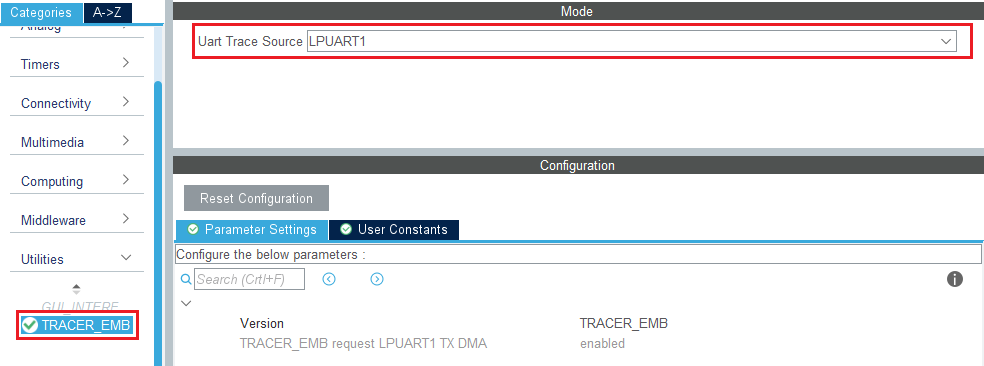
3.10.2. Configure embedded tracer
In the utilities section, select TRACER_EMB and use LPUART1 as the trace source.
Then, go back to the USBPD middleware configuration and check the tracer source checkbox.
3.10.3. Configure UCPD monitor firmware responder for debug
The firmware interactive stack responder can be activated if interaction with the USB PD stack is needed, using the UCPD monitor tool STM32CubeMonUCPD[7]. In the utilities section, enable GUI_INTERFACE, then enter free text to describe the board.
4. Configure project
![]() 5min
5min
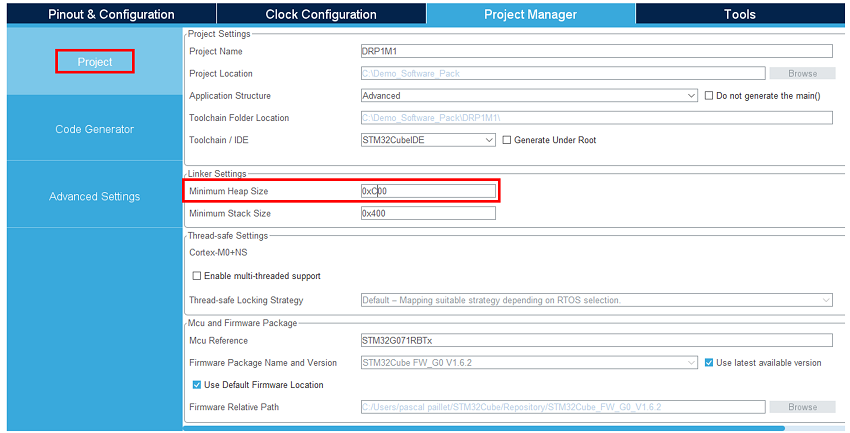
Under the project manager main tab, configure the minimum stack size to 0xC00 under the project tab. This is a first value, which can be tuned later, depending on application needs.
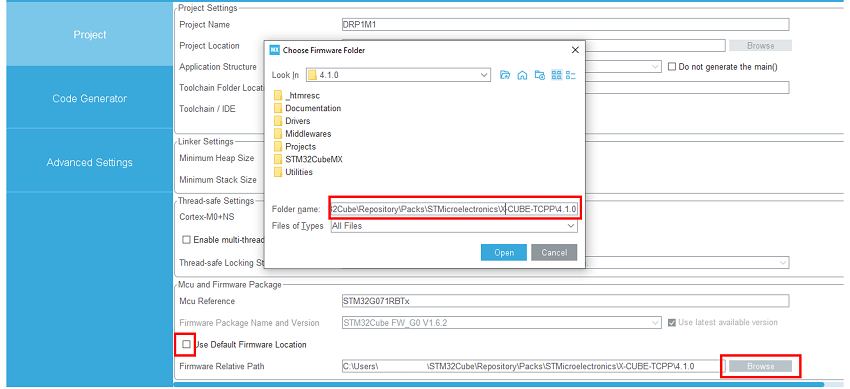
For the STM32G0 or G4 MCU, uncheck “use default firmware location” and instead, select the software pack “c:|\user\ … \STM32Cube\Repositoryctronics/Packs\STMicroelectronics\X-CUBE-TCPP\V4.1.0\” as firmware location to be sure to use the latest USB PD lib releases as the standard evolution is very fast.
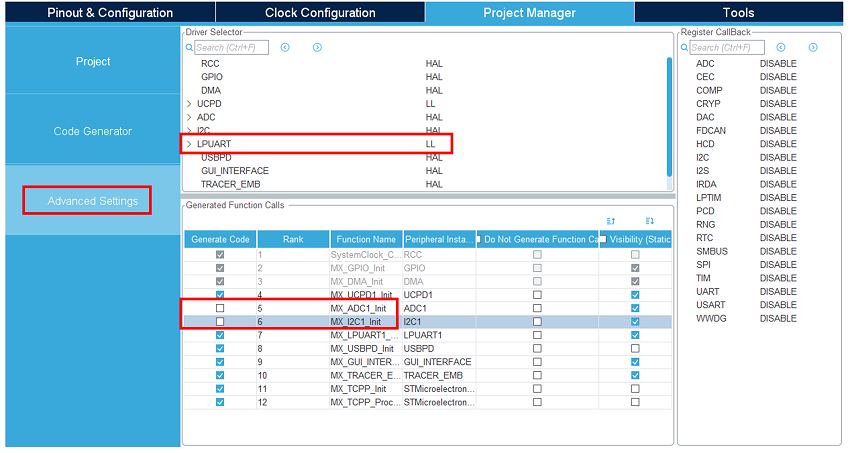
Under the advanced settings tab, change the LPUART driver to LL to save a bit of memory heap size. As we do not need the ADC and I2C initialization functions (handled by the BSP drivers), uncheck generate code for the MX_I2C2_Init and MX_ADC1_Init functions.
5. Generate code
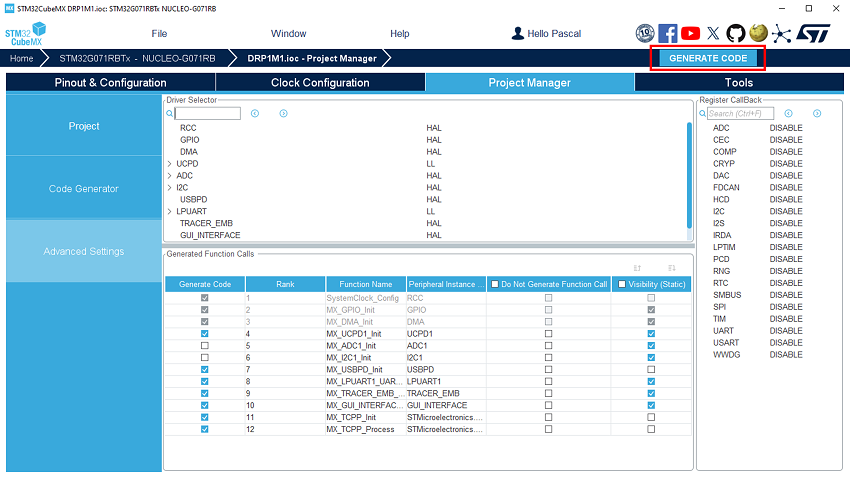
Save your file with ctrl+s and select generate code.
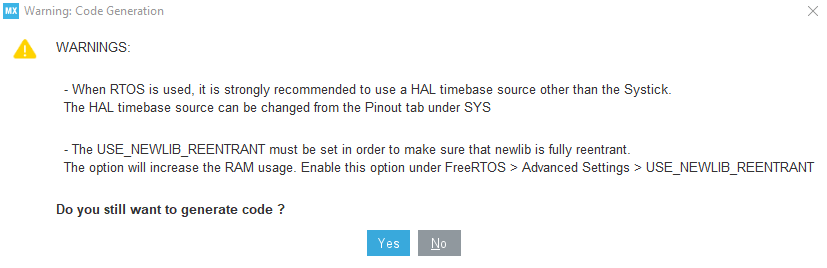
A warning appears, informing that a proper HAL timebase is not defined. It is safer to use a dedicated timer as a HAL timebase source.
For this demonstration, the below warning can be ignored by clicking yes.
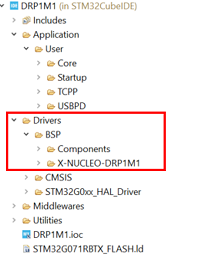
In this project, different folders can be found:
- The USBPD folder contains the source files that we need to edit to enrich the power delivery application.
- The core folder contains the source files for the core of the project.
- The drivers folder contains the HAL drivers for the STM32, and the BSP for the Nucleo board and X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield.
- The middleware folder contains the source files and the libraries for FreeRTOS™ and USB PD.
- The utilities folder contains the GUI (UCPD monitor) and tracer embedded source files part.
The drivers folder in the explorer view of the project must contain the BSP folders added earlier.
6. Configure the shield's jumpers
No jumper is needed on the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield.
7. Compile and run the application
The compilation must be performed without errors or warnings.
Build the application by clicking on the ![]() button (or select project/build project).
button (or select project/build project).
Run the application by clicking on the ![]() button (or select run/run).
button (or select run/run).
8. Establish the first explicit contract
![]() 5min
5min
With your application running on the board, launch the STM32CubeMonitor-UCPD application.
The user's board must appear in the list when clicking "refresh list of connected boards", so double-click on the
corresponding line (or click "NEXT").
Note: The ComPort may be different. It depends on the number of boards installed on the computer. Then double-click on the desired UCPD port, here port 0, or select it and click "NEXT".
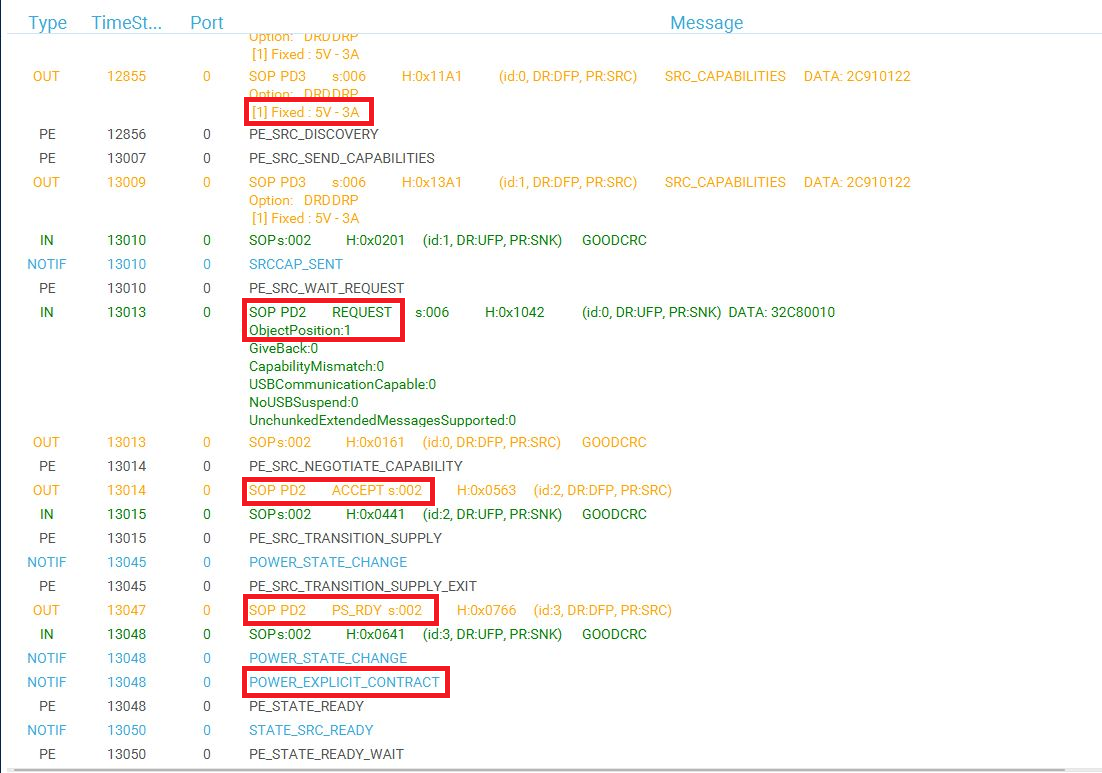
Click on the TRACES button in the bottom right corner to get protocol traces. You can then plug a power delivery sink into the USB Type-C® receptacle of the X-NUCLEO-DRP1M1 shield. The screen may look like this:
The figure above shows the communication between the STM32G0 and the power delivery sink on the right panel. It is possible to verify the correct sequence to reach an explicit contract:
- The capabilities are sent by the STM32G0 drp (OUT orange message).
- The request is sent by the sink (IN green message).
- The ACCEPT and the PS_RDY are sent by the STM32G0 source (OUT orange message).
- The contract negotiation ends by the POWER_EXPLICIT_CONTRACT notification (blue message).
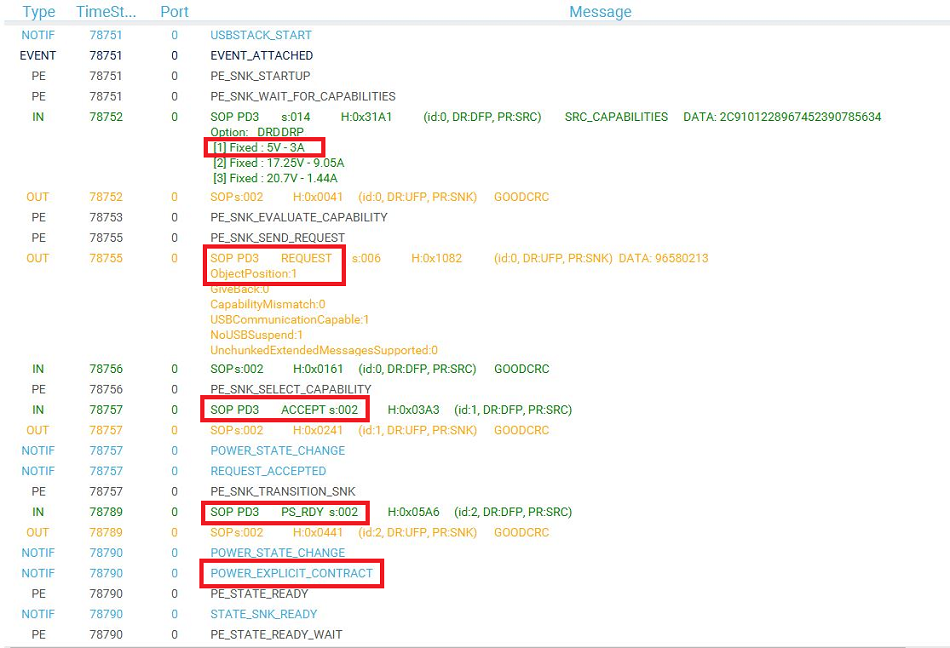
The figure above shows the communication between the STM32G0 and the power delivery source on the right panel. It is possible to verify the correct sequence to reach an explicit contract:
- The capabilities are sent by the source (IN green message).
- The request is sent by the STM32G0 drp (OUT orange message).
- The ACCEPT and the PS_RDY are sent by the source (IN green message).
- The contract negotiation ends by the POWER_EXPLICIT_CONTRACT notification (blue message).
For more details on how to use this tool, refer to UM2468. And for more details on the protocol, refer to UM2552. Note that this trace is very helpful for debugging and application development.
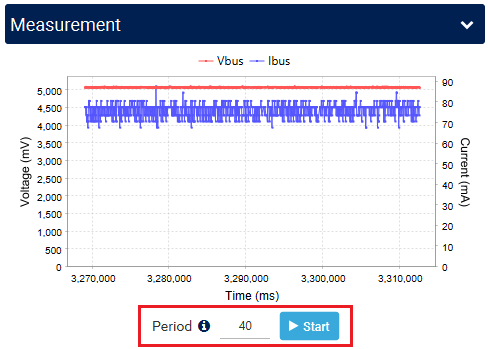
You can also use the measurement window in STM32CubeMonitor-UCPD to display a graph of the measured VBUS voltage and delivered current. Set the sampling period and click start.
9. Information focus: Code inserted by the software pack
By enabling the software pack in section 3.8, the code below has been added automatically in the following files:
| usbpd_dpm_user_h |
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Typedef */ tags:
#if !defined(USBPD_REV_MAJOR)
#define USBPD_REV_MAJOR (3U) /* USBPD Specification revision major */
#define USBPD_REV_MINOR (1U) /* USBPD Specification revision minor */
#define USBPD_VERSION_MAJOR (1U) /* USBPD Specification version major */
#define USBPD_VERSION_MINOR (7U) /* USBPD Specification version minor */
#endif /* !USBPD_REV_MAJOR */
/** @brief USBPD PDO Selection method enum definition
*
*/
typedef enum
{
PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_PWR,
PDO_SEL_METHOD_MIN_PWR,
PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_VOLT,
PDO_SEL_METHOD_MIN_VOLT,
PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_CUR,
PDO_SEL_METHOD_MIN_CUR
} USBPD_DPM_PDO_SelectionMethodTypeDef;
typedef enum {
DPM_USER_EVENT_TIMER, /* TIMER EVENT */
DPM_USER_EVENT_GUI, /* GUI EVENT */
DPM_USER_EVENT_NONE, /* NO EVENT */
} DPM_USER_EVENT;
/**
* @brief USBPD DPM handle Structure definition
* @{
*/
typedef struct
{
uint32_t DPM_ListOfRcvSNKPDO[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO]; /*!< The list of received Sink Power Data Objects from Port partner (when Port partner is a Sink or a DRP port). */
uint32_t DPM_NumberOfRcvSNKPDO; /*!< The number of received Sink Power Data Objects from port Partner (when Port partner is a Sink or a DRP port). */
uint32_t DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO]; /*!< The list of received Source Power Data Objects from Port partner */
uint32_t DPM_NumberOfRcvSRCPDO; /*!< The number of received Source Power Data Objects from port Partner (when Port partner is a Source or a DRP port). */
uint32_t DPM_RcvRequestDOMsg; /*!< Received request Power Data Object message from the port Partner */
uint32_t DPM_RequestDOMsgPrevious; /*!< Previous Request Power Data Object message to be sent */
USBPD_PPSSDB_TypeDef DPM_RcvPPSStatus; /*!< PPS Status received by port partner */
USBPD_SKEDB_TypeDef DPM_RcvSNKExtendedCapa; /*!< SNK Extended Capability received by port partner */
uint32_t DPM_RequestDOMsg; /*!< Request Power Data Object message to be sent */
uint32_t DPM_RDOPosition; /*!< RDO Position of requested DO in Source list of capabilities */
uint32_t DPM_RDOPositionPrevious; /*!< RDO Position of previous requested DO in Source list of capabilities */
uint32_t DPM_RequestedVoltage; /*!< Value of requested voltage */
uint32_t DPM_RequestedCurrent; /*!< Value of requested current */
int16_t DPM_MeasuredCurrent; /*!< Value of measured current */
volatile uint32_t DPM_ErrorCode; /*!< USB PD Error code */
volatile uint8_t DPM_IsConnected; /*!< USB PD connection state */
uint16_t DPM_Reserved:14; /*!< Reserved bytes */
#if defined(_GUI_INTERFACE)
volatile uint16_t DPM_TimerMeasReport; /*!< Timer used to send measurement report */
#endif /* _GUI_INTERFACE */
} USBPD_HandleTypeDef;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Define */ tags: #define DPM_NO_SRC_PDO_FOUND 0xFFU /*!< No match found between Received SRC PDO and SNK capabilities */
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Variables */ tags: #if !defined(USBPD_DPM_USER_C)
extern USBPD_HandleTypeDef DPM_Ports[USBPD_PORT_COUNT];
#else
USBPD_HandleTypeDef DPM_Ports[USBPD_PORT_COUNT] =
{
{
.DPM_Reserved = 0,
#if defined(USBPDCORE_SNK_CAPA_EXT)
.DPM_RcvSNKExtendedCapa = {0}, /*!< SNK Extended Capability received by port partner */
#endif /* USBPDCORE_SNK_CAPA_EXT */
}
};
#endif /* !USBPD_DPM_USER_C */
|
| usbpd_dpm_user_c |
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Includes */ tags:
#if !defined(_TRACE)
#include "string.h"
#endif /* !_TRACE */
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Typedef */ tags: /** @brief Sink Request characteritics Structure definition
*
*/
typedef struct
{
uint32_t RequestedVoltageInmVunits; /*!< Sink request operating voltage in mV units */
uint32_t MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits; /*!< Sink request Max operating current in mA units */
uint32_t OperatingCurrentInmAunits; /*!< Sink request operating current in mA units */
uint32_t MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits; /*!< Sink request Max operating power in mW units */
uint32_t OperatingPowerInmWunits; /*!< Sink request operating power in mW units */
} USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Variables */ tags: /* Method used to find the "best" PDO */
USBPD_DPM_PDO_SelectionMethodTypeDef USBPD_DPM_PDO_Sel_Method = PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_PWR;
USBPD_HandleTypeDef DPM_Ports[USBPD_PORT_COUNT];
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Prototypes */ tags: static void DPM_SNK_BuildRDOfromSelectedPDO(uint8_t PortNum, uint8_t IndexSrcPDO, USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef* PtrRequestPowerDetails,
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef* Rdo, USBPD_CORE_PDO_Type_TypeDef *PtrPowerObject);
static uint32_t DPM_FindVoltageIndex(uint32_t PortNum, USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef* PtrRequestPowerDetails, uint8_t Method);
static void DPM_AssertRp(uint8_t PortNum);
static void DPM_AssertRd(uint8_t PortNum);
static USBPD_StatusTypeDef DPM_TurnOnPower(uint8_t PortNum, USBPD_PortPowerRole_TypeDef Role);
static USBPD_StatusTypeDef DPM_TurnOffPower(uint8_t PortNum, USBPD_PortPowerRole_TypeDef Role);
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_UserInit */ tags: /* PWR SET UP */
if(USBPD_OK != USBPD_PWR_IF_Init())
{
return USBPD_ERROR;
}
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_UserCableDetection */ tags: #ifdef _GUI_INTERFACE
switch(State)
{
case USBPD_CAD_EVENT_ATTEMC:
case USBPD_CAD_EVENT_ATTACHED:
/* Format and send a notification to GUI if enabled */
if (NULL != DPM_GUI_FormatAndSendNotification)
{
DPM_GUI_FormatAndSendNotification(PortNum, DPM_GUI_NOTIF_ISCONNECTED, 0);
}
break;
default :
/* Format and send a notification to GUI if enabled */
if (NULL != DPM_GUI_FormatAndSendNotification)
{
DPM_GUI_FormatAndSendNotification(PortNum, DPM_GUI_NOTIF_ISCONNECTED | DPM_GUI_NOTIF_POWER_EVENT, 0);
}
}
#endif /*_GUI_INTERFACE*/
switch(State)
{
case USBPD_CAD_EVENT_ATTACHED:
case USBPD_CAD_EVENT_ATTEMC:
{
if (DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_PowerRole == USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC)
{
if (USBPD_OK != USBPD_PWR_IF_VBUSEnable(PortNum))
{
/* Should not occur */
NVIC_SystemReset();
}
}
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_IsConnected = 1;
break;
}
case USBPD_CAD_EVENT_DETACHED :
case USBPD_CAD_EVENT_EMC :
default :
if (DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_PowerRole == USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC)
{
if (USBPD_OK != USBPD_PWR_IF_VBUSDisable(PortNum))
{
/* Should not occur */
while(1);
}
}
/* reset all values received from port partner */
memset(&DPM_Ports[PortNum], 0, sizeof(DPM_Ports[PortNum]));
break;
}
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_HardReset */ tags: switch (Status)
{
case USBPD_HR_STATUS_WAIT_VBUS_VSAFE0V:
if (USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC == CurrentRole)
{
/* Reset the power supply */
DPM_TurnOffPower(PortNum, USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC);
}
break;
case USBPD_HR_STATUS_WAIT_VBUS_VSAFE5V:
if (CurrentRole == USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC)
{
/* Power on the power supply */
DPM_TurnOnPower(PortNum, CurrentRole);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_GetDataInfo */ tags: /* Case Port Source PDO Data information : */
/* Case Port SINK PDO Data information : */
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SRC_PDO :
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SNK_PDO :
USBPD_PWR_IF_GetPortPDOs(PortNum, DataId, Ptr, Size);
*Size *= 4;
break;
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_REQ_VOLTAGE :
*Size = 4;
(void)memcpy((uint8_t*)Ptr, (uint8_t *)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedVoltage, *Size);
break;
case USBPD_CORE_REVISION:
{
*Size = sizeof(USBPD_RevisionDO_TypeDef);
USBPD_RevisionDO_TypeDef rev =
{
/* Hardcoded values, user should use a global USBPD_RevisionDO_TypeDef variable */
.b.Revision_major = USBPD_REV_MAJOR, /*!< Major revision */
.b.Revision_minor = USBPD_REV_MINOR, /*!< Minor revision */
.b.Version_major = USBPD_VERSION_MAJOR, /*!< Major version */
.b.Version_minor = USBPD_VERSION_MINOR /*!< Minor version */
};
memcpy((uint8_t *)Ptr, &rev, *Size);
break;
}
case USBPD_CORE_PPS_STATUS :
{
/* Get current drawn by sink */
USBPD_PPSSDB_TypeDef pps_status = {0};
*Size = 4;
(void)memcpy((uint8_t*)Ptr, (uint8_t *)&pps_status.d32, *Size);
}
break;
#if defined (USBPD_CORE_SNK_EXTENDED_CAPA)
case USBPD_CORE_SNK_EXTENDED_CAPA :
{
*Size = sizeof(USBPD_SKEDB_TypeDef);
memcpy((uint8_t*)Ptr, (uint8_t *)&DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum].DPM_SNKExtendedCapa, *Size);
}
break;
#endif /* USBPD_CORE_SNK_EXTENDED_CAPA */
default:
break;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_SetDataInfo */ tags: /* Case Received Request PDO Data information : */
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_RDO_POSITION :
if (Size == 4)
{
uint8_t* temp;
temp = (uint8_t*)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RDOPosition;
(void)memcpy(temp, Ptr, Size);
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RDOPositionPrevious = *Ptr;
temp = (uint8_t*)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RDOPositionPrevious;
(void)memcpy(temp, Ptr, Size);
}
break;
/* Case Received Sink PDO values Data information :*/
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_RCV_SNK_PDO :
if (Size <= (USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO * 4))
{
uint8_t* rdo;
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_NumberOfRcvSNKPDO = (Size / 4);
/* Copy PDO data in DPM Handle field */
for (uint32_t index = 0; index < (Size / 4); index++)
{
rdo = (uint8_t*)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_ListOfRcvSNKPDO[index];
(void)memcpy(rdo, (Ptr + (index * 4u)), (4u * sizeof(uint8_t)));
}
}
break;
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_RCV_REQ_PDO : /*!< Storage of Received Sink Request PDO value */
if (Size == 4)
{
memcpy((uint8_t *)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RcvRequestDOMsg, Ptr, 4);
}
break;
/* Case Received Source PDO values Data information : */
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_RCV_SRC_PDO :
if (Size <= (USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO * 4))
{
uint8_t* rdo;
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_NumberOfRcvSRCPDO = (Size / 4);
/* Copy PDO data in DPM Handle field */
for (uint32_t index = 0; index < (Size / 4); index++)
{
rdo = (uint8_t*)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[index];
(void)memcpy(rdo, (Ptr + (index * 4u)), (4u * sizeof(uint8_t)));
}
}
break;
case USBPD_CORE_PPS_STATUS :
{
uint8_t* ext_capa;
ext_capa = (uint8_t*)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RcvPPSStatus;
memcpy(ext_capa, Ptr, Size);
}
case USBPD_CORE_REVISION:
{
/* Does nothing: User have to implement a global revision variable */
USBPD_RevisionDO_TypeDef rev = {0};
memcpy((uint8_t *)&rev, Ptr, sizeof(USBPD_RevisionDO_TypeDef));
break;
}
#if defined(USBPDCORE_SNK_CAPA_EXT)
case USBPD_CORE_SNK_EXTENDED_CAPA :
{
uint8_t* _snk_ext_capa;
_snk_ext_capa = (uint8_t*)&DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RcvSNKExtendedCapa;
memcpy(_snk_ext_capa, Ptr, Size);
}
#endif /* USBPDCORE_SNK_CAPA_EXT */
default:
break;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_EvaluateRequest */ tags: USBPD_StatusTypeDef _retr = USBPD_REJECT;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef rdo;
/* read the request value received */
rdo.d32 = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RcvRequestDOMsg;
/* Search PDO in Port Source PDO list, that corresponds to Position provided in Request RDO */
if (USBPD_PWR_IF_SearchRequestedPDO(PortNum, rdo.GenericRDO.ObjectPosition, &pdo.d32) == USBPD_OK)
{
/* Evaluate the request */
if(pdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject == USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED)
{
if((rdo.FixedVariableRDO.OperatingCurrentIn10mAunits > pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits)
|| ((rdo.FixedVariableRDO.MaxOperatingCurrent10mAunits > pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits)&&(rdo.FixedVariableRDO.CapabilityMismatch==0)))
{
/* Sink requests too much maximum operating current */
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateRequest: Sink requests too much maximum operating current */
_retr = USBPD_REJECT;
}
else
{
/* Save the power object */
*PtrPowerObject = pdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject;
/* Set RDO position and requested voltage in DPM port structure */
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedVoltage = pdo.SRCFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits * 50;
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RDOPositionPrevious = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RDOPosition;
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RDOPosition = rdo.GenericRDO.ObjectPosition;
_retr = USBPD_ACCEPT;
}
}
}
return _retr;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_SNK_EvaluateCapabilities */ tags: USBPD_PDO_TypeDef fixed_pdo;
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef rdo;
USBPD_HandleTypeDef *pdhandle = &DPM_Ports[PortNum];
USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *puser = (USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *)&DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum];
USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef snkpowerrequestdetails;
uint32_t pdoindex, size;
uint32_t snkpdolist[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO];
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef snk_fixed_pdo;
snkpowerrequestdetails.RequestedVoltageInmVunits = 0;
snkpowerrequestdetails.OperatingCurrentInmAunits = 0;
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateCapabilities: Port Partner Requests Max Voltage */
/* Find the Pdo index for the requested voltage */
pdoindex = DPM_FindVoltageIndex(PortNum, &snkpowerrequestdetails, USBPD_DPM_PDO_Sel_Method);
/* Initialize RDO */
rdo.d32 = 0;
/* If no valid SNK PDO or if no SRC PDO match found (index>=nb of valid received SRC PDOs or function returned DPM_NO_SRC_PDO_FOUND*/
if (pdoindex >= pdhandle->DPM_NumberOfRcvSRCPDO)
{
#if defined(_TRACE)
USBPD_TRACE_Add(USBPD_TRACE_DEBUG, PortNum, 0, (uint8_t *) "PE_EvaluateCapability: could not find desired voltage", sizeof("PE_EvaluateCapability: could not find desired voltage"));
#endif /* _TRACE */
fixed_pdo.d32 = pdhandle->DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[0];
/* Read SNK PDO list for retrieving useful data to fill in RDO */
USBPD_PWR_IF_GetPortPDOs(PortNum, USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SNK_PDO, (uint8_t*)&snkpdolist[0], &size);
/* Store value of 1st SNK PDO (Fixed) in local variable */
snk_fixed_pdo.d32 = snkpdolist[0];
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.ObjectPosition = 1;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.OperatingCurrentIn10mAunits = fixed_pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.MaxOperatingCurrent10mAunits = fixed_pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.CapabilityMismatch = 1;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.USBCommunicationsCapable = snk_fixed_pdo.SNKFixedPDO.USBCommunicationsCapable;
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedCurrent = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits;
pdhandle->DPM_RequestDOMsg = rdo.d32;
*PtrPowerObjectType = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED;
*PtrRequestData = rdo.d32;
pdhandle->DPM_RequestedVoltage = 5000;
return;
}
DPM_SNK_BuildRDOfromSelectedPDO(PortNum, pdoindex, &snkpowerrequestdetails,&rdo, PtrPowerObjectType);
*PtrRequestData = pdhandle->DPM_RequestDOMsg;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_PowerRoleSwap */ tags: switch (Status)
{
case USBPD_PRS_STATUS_VBUS_OFF:
if (CurrentRole == USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC)
{
#if defined(_VCONN_SUPPORT)
/* This variable is used to avoid VCONN disable during HR procedure */
uint32_t _vconnstate = DPM_Params[PortNum].VconnStatus;
DPM_Params[PortNum].VconnStatus = USBPD_FALSE;
#endif /* _VCONN_SUPPORT */
/* In case of power role swap keep VCONN On */
DPM_TurnOffPower(PortNum, CurrentRole);
#if defined(_VCONN_SUPPORT)
/* restore vconn status */
DPM_Params[PortNum].VconnStatus = _vconnstate;
#endif /* _VCONN_SUPPORT */
}
break;
case USBPD_PRS_STATUS_SRC_RP2RD:
DPM_AssertRd(PortNum);
USBPD_DPM_WaitForTime(5);
break;
case USBPD_PRS_STATUS_SNK_RD2RP:
DPM_AssertRp(PortNum);
break;
case USBPD_PRS_STATUS_VBUS_ON:
DPM_TurnOnPower(PortNum, CurrentRole);
break;
default:
break;
}
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_DPM_RequestMessageRequest */ tags: /* To be adapted to call the PE function */
/* _status = USBPD_PE_Send_Request(PortNum, rdo.d32, pdo_object);*/
uint32_t voltage, allowablepower;
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef rdo;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
USBPD_CORE_PDO_Type_TypeDef pdo_object;
USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *puser = (USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *)&DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum];
USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef request_details;
rdo.d32 = 0;
/* selected SRC PDO */
pdo.d32 = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[(IndexSrcPDO - 1)];
voltage = RequestedVoltage;
allowablepower = (puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits * RequestedVoltage) / 1000U;
if (USBPD_TRUE == USBPD_DPM_SNK_EvaluateMatchWithSRCPDO(PortNum, pdo.d32, &voltage, &allowablepower))
{
/* Check that voltage has been correctly selected */
if (RequestedVoltage == voltage)
{
request_details.RequestedVoltageInmVunits = RequestedVoltage;
request_details.OperatingCurrentInmAunits = (1000U * allowablepower)/RequestedVoltage;
request_details.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits;
request_details.MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits;
request_details.OperatingPowerInmWunits = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.OperatingPowerInmWunits;
DPM_SNK_BuildRDOfromSelectedPDO(PortNum, (IndexSrcPDO - 1), &request_details, &rdo, &pdo_object);
_status = USBPD_PE_Send_Request(PortNum, rdo.d32, pdo_object);
}
}
/* USER CODE END USBPD_DPM_RequestMessageRequest */
return _status;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_USER_PRIVATE_FUNCTIONS */ tags: /**
* @brief Examinate a given SRC PDO to check if matching with SNK capabilities.
* @param PortNum Port number
* @param SrcPDO Selected SRC PDO (32 bits)
* @param PtrRequestedVoltage Pointer on Voltage value that could be reached if SRC PDO is requested (only valid if USBPD_TRUE is returned) in mV
* @param PtrRequestedPower Pointer on Power value that could be reached if SRC PDO is requested (only valid if USBPD_TRUE is returned) in mW
* @retval USBPD_FALSE of USBPD_TRUE (USBPD_TRUE returned in SRC PDO is considered matching with SNK profile)
*/
uint32_t USBPD_DPM_SNK_EvaluateMatchWithSRCPDO(uint8_t PortNum, uint32_t SrcPDO, uint32_t* PtrRequestedVoltage, uint32_t* PtrRequestedPower)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef srcpdo, snkpdo;
uint32_t match = USBPD_FALSE;
uint32_t nbsnkpdo;
uint32_t snkpdo_array[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO];
uint16_t i, srcvoltage50mv, srcmaxvoltage50mv, srcminvoltage50mv, srcmaxcurrent10ma;
uint16_t snkvoltage50mv, snkmaxvoltage50mv, snkminvoltage50mv, snkopcurrent10ma;
uint32_t maxrequestedpower, currentrequestedpower;
uint32_t maxrequestedvoltage, currentrequestedvoltage;
uint32_t snkoppower250mw, srcmaxpower250mw;
/* Retrieve SNK PDO list from PWR_IF storage : PDO values + nb of u32 written by PWR_IF (nb of PDOs) */
USBPD_PWR_IF_GetPortPDOs(PortNum, USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SNK_PDO, (uint8_t*)snkpdo_array, &nbsnkpdo);
if (0 == nbsnkpdo)
{
return(USBPD_FALSE);
}
/* Set default output values */
maxrequestedpower = 0;
maxrequestedvoltage = 0;
/* Check SRC PDO value according to its type */
srcpdo.d32 = SrcPDO;
switch(srcpdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
/* SRC Fixed Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED:
srcvoltage50mv = srcpdo.SRCFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits;
srcmaxcurrent10ma = srcpdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits;
/* Loop through SNK PDO list */
for (i=0; i<nbsnkpdo; i++)
{
currentrequestedpower = 0;
currentrequestedvoltage = 0;
/* Retrieve SNK PDO value according to its type */
snkpdo.d32 = snkpdo_array[i];
switch(snkpdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
/* SNK Fixed Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED:
{
snkvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits;
snkopcurrent10ma = snkpdo.SNKFixedPDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Voltage = SRC Voltage
&&
SNK Op Current <= SRC Max Current
Requested Voltage : SNK Voltage
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Current
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Current
*/
if ( (snkvoltage50mv == srcvoltage50mv)
&&(snkopcurrent10ma <= srcmaxcurrent10ma))
{
currentrequestedpower = (snkvoltage50mv * snkopcurrent10ma) / 2; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = snkvoltage50mv;
}
break;
}
/* SNK Variable Supply (non-battery) PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE:
snkmaxvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkminvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkopcurrent10ma = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Max voltage >= SRC Voltage
&&
SNK Min voltage <= SRC Voltage
&&
SNK Op current <= SRC Max current
Requested Voltage : SRC Voltage
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Current
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Current
*/
if ( (snkmaxvoltage50mv >= srcvoltage50mv)
&&(snkminvoltage50mv <= srcvoltage50mv)
&&(snkopcurrent10ma <= srcmaxcurrent10ma))
{
currentrequestedpower = (srcvoltage50mv * snkopcurrent10ma) / 2; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = srcvoltage50mv;
}
break;
/* SNK Battery Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY:
snkmaxvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkminvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkoppower250mw = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.OperationalPowerIn250mWunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Max voltage >= SRC Voltage
&&
SNK Min voltage <= SRC Voltage
&&
SNK Op power <= SRC Max current * SRC Voltage
Requested Voltage : SRC Voltage
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Power/ SRC Voltage
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Power/ SRC Voltage
*/
if ( (snkmaxvoltage50mv >= srcvoltage50mv)
&&(snkminvoltage50mv <= srcvoltage50mv)
&&(snkoppower250mw <= ((srcvoltage50mv * srcmaxcurrent10ma)/500))) /* to get value in 250 mw units */
{
currentrequestedvoltage = srcvoltage50mv;
currentrequestedpower = snkoppower250mw;
}
break;
/* SNK Augmented Power Data Object (APDO) */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO:
break;
default:
break;
}
if (currentrequestedpower > maxrequestedpower)
{
match = USBPD_TRUE;
maxrequestedpower = currentrequestedpower;
maxrequestedvoltage = currentrequestedvoltage;
}
}
break;
/* SRC Variable Supply (non-battery) PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE:
srcmaxvoltage50mv = srcpdo.SRCVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
srcminvoltage50mv = srcpdo.SRCVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
srcmaxcurrent10ma = srcpdo.SRCVariablePDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits;
/* Loop through SNK PDO list */
for (i=0; i<nbsnkpdo; i++)
{
currentrequestedpower = 0;
currentrequestedvoltage = 0;
/* Retrieve SNK PDO value according to its type */
snkpdo.d32 = snkpdo_array[i];
switch(snkpdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
/* SNK Fixed Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED:
/* No match */
break;
/* SNK Variable Supply (non-battery) PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE:
snkmaxvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkminvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkopcurrent10ma = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Max voltage >= SRC Max Voltage
&&
SNK Min voltage <= SRC Min Voltage
&&
SNK Op current <= SRC Max current
Requested Voltage : Any value between SRC Min Voltage and SRC Max Voltage
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Current
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Current
*/
if ( (snkmaxvoltage50mv >= srcmaxvoltage50mv)
&&(snkminvoltage50mv <= srcminvoltage50mv)
&&(snkopcurrent10ma <= srcmaxcurrent10ma))
{
currentrequestedpower = (srcmaxvoltage50mv * snkopcurrent10ma) / 2; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = srcmaxvoltage50mv;
}
break;
/* SNK Battery Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY:
snkmaxvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkminvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkoppower250mw = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.OperationalPowerIn250mWunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Max voltage >= SRC Max Voltage
&&
SNK Min voltage <= SRC Min Voltage
&&
SNK Op power <= SRC Max current * SRC Max Voltage
Requested Voltage : Any value between SRC Min Voltage and SRC Max Voltage, that fulfill
SNK Op power <= Voltage * SRC Max Current
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Power/ SRC Voltage
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Power/ SRC Voltage
*/
if ( (snkmaxvoltage50mv >= srcmaxvoltage50mv)
&&(snkminvoltage50mv <= srcminvoltage50mv)
&&(snkoppower250mw <= ((srcmaxvoltage50mv * srcmaxcurrent10ma)/500))) /* to get value in 250 mw units */
{
currentrequestedpower = snkoppower250mw * 250; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = srcmaxvoltage50mv;
}
break;
/* SNK Augmented Power Data Object (APDO) */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO:
break;
default:
break;
}
if (currentrequestedpower > maxrequestedpower)
{
match = USBPD_TRUE;
maxrequestedpower = currentrequestedpower;
maxrequestedvoltage = currentrequestedvoltage;
}
}
break;
/* SRC Battery Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY:
srcmaxvoltage50mv = srcpdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
srcminvoltage50mv = srcpdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
srcmaxpower250mw = srcpdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MaxAllowablePowerIn250mWunits;
/* Loop through SNK PDO list */
for (i=0; i<nbsnkpdo; i++)
{
currentrequestedpower = 0;
currentrequestedvoltage = 0;
/* Retrieve SNK PDO value according to its type */
snkpdo.d32 = snkpdo_array[i];
switch(snkpdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
/* SNK Fixed Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED:
/* No match */
break;
/* SNK Variable Supply (non-battery) PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE:
snkmaxvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkminvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkopcurrent10ma = snkpdo.SNKVariablePDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Max voltage >= SRC Max Voltage
&&
SNK Min voltage <= SRC Min Voltage
&&
SNK Op current * SRC Max Voltage <= SRC Max Power
Requested Voltage : Any value between SRC Min Voltage and SRC Max Voltage : SRC Max Voltage
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Current
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Current
*/
if ( (snkmaxvoltage50mv >= srcmaxvoltage50mv)
&&(snkminvoltage50mv <= srcminvoltage50mv)
&&(srcmaxvoltage50mv * snkopcurrent10ma <= srcmaxpower250mw))
{
currentrequestedpower = (srcmaxvoltage50mv * snkopcurrent10ma) / 2; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = srcmaxvoltage50mv;
}
break;
/* SNK Battery Supply PDO */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY:
snkmaxvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkminvoltage50mv = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits;
snkoppower250mw = snkpdo.SNKBatteryPDO.OperationalPowerIn250mWunits;
/* Match if :
SNK Max voltage >= SRC Max Voltage
&&
SNK Min voltage <= SRC Min Voltage
&&
SNK Op power <= SRC Max power
Requested Voltage : Any value between SRC Min Voltage and SRC Max Voltage, that fulfill
SNK Op power <= Voltage * SRC Max Current
Requested Op Current : SNK Op Power/ SRC Voltage
Requested Max Current : SNK Op Power/ SRC Voltage
*/
if ( (snkmaxvoltage50mv >= srcmaxvoltage50mv)
&&(snkminvoltage50mv <= srcminvoltage50mv)
&&(snkoppower250mw <= srcmaxpower250mw))
{
currentrequestedpower = snkoppower250mw * 250; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = srcmaxvoltage50mv;
}
break;
/* SNK Augmented Power Data Object (APDO) */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO:
break;
default:
break;
}
if (currentrequestedpower > maxrequestedpower)
{
match = USBPD_TRUE;
maxrequestedpower = currentrequestedpower;
maxrequestedvoltage = currentrequestedvoltage;
}
}
break;
/* Augmented Power Data Object (APDO) */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO:
{
uint16_t srcmaxvoltage100mv, srcmaxcurrent50ma;
srcmaxvoltage100mv = srcpdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxVoltageIn100mV;
srcmaxcurrent50ma = srcpdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxCurrentIn50mAunits;
/* Loop through SNK PDO list */
for (i=0; i<nbsnkpdo; i++)
{
currentrequestedpower = 0;
currentrequestedvoltage = 0;
/* Retrieve SNK PDO value according to its type */
snkpdo.d32 = snkpdo_array[i];
switch(snkpdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED:
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE:
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY:
/* No match */
break;
/* SNK Augmented Power Data Object (APDO) */
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO:
{
uint16_t snkmaxvoltage100mv, snkminvoltage100mv, snkmaxcurrent50ma;
snkminvoltage100mv = snkpdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MinVoltageIn100mV;
snkmaxvoltage100mv = snkpdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxVoltageIn100mV;
snkmaxcurrent50ma = snkpdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxCurrentIn50mAunits;
/* Match if voltage matches with the APDO voltage range */
if ((PWR_DECODE_100MV(snkminvoltage100mv) <= (*PtrRequestedVoltage))
&& ((*PtrRequestedVoltage) <= PWR_DECODE_100MV(snkmaxvoltage100mv))
&& (snkmaxcurrent50ma <= srcmaxcurrent50ma))
{
if (0 != *PtrRequestedPower)
{
currentrequestedpower = (*PtrRequestedVoltage * PWR_DECODE_50MA(snkmaxcurrent50ma)) / 1000; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = (*PtrRequestedVoltage / 50);
}
else
{
*PtrRequestedVoltage = MIN(PWR_DECODE_100MV(srcmaxvoltage100mv), PWR_DECODE_100MV(snkmaxvoltage100mv));
currentrequestedpower = (*PtrRequestedVoltage * PWR_DECODE_50MA(snkmaxcurrent50ma)) / 1000; /* to get value in mw */
currentrequestedvoltage = (*PtrRequestedVoltage / 50);
}
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
if (currentrequestedpower > maxrequestedpower)
{
match = USBPD_TRUE;
maxrequestedpower = currentrequestedpower;
maxrequestedvoltage = currentrequestedvoltage;
}
}
}
break;
default:
return(USBPD_FALSE);
}
if (maxrequestedpower > 0)
{
*PtrRequestedPower = maxrequestedpower;
*PtrRequestedVoltage = maxrequestedvoltage * 50; /* value in mV */
}
return(match);
}
/**
* @brief Find PDO index that offers the most amount of power and in accordance with SNK capabilities.
* @param PortNum Port number
* @param PtrRequestPowerDetails Sink requested power details structure pointer
* @retval Index of PDO within source capabilities message (DPM_NO_SRC_PDO_FOUND indicating not found)
*/
static uint32_t DPM_FindVoltageIndex(uint32_t PortNum, USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef* PtrRequestPowerDetails, uint8_t Method)
{
uint32_t *ptpdoarray;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
uint32_t voltage;
uint32_t reqvoltage;
uint32_t nbpdo;
uint32_t allowablepower;
uint32_t selpower;
uint32_t allowablecurrent;
uint32_t selcurrent;
uint32_t curr_index = DPM_NO_SRC_PDO_FOUND;
uint32_t temp_index;
USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *puser = (USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *)&DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum];
allowablepower = 0;
selpower = 0;
reqvoltage = 0;
voltage = 0;
selcurrent = 0;
/* Search PDO index among Source PDO of Port */
nbpdo = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_NumberOfRcvSRCPDO;
ptpdoarray = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO;
/* search the best PDO in the list of source PDOs */
for (temp_index = 0; temp_index < nbpdo; temp_index++)
{
pdo.d32 = ptpdoarray[temp_index];
/* Check if the received source PDO is matching any of the SNK PDO */
allowablepower = 0;
if (USBPD_TRUE == USBPD_DPM_SNK_EvaluateMatchWithSRCPDO(PortNum, pdo.d32, &voltage, &allowablepower))
{
allowablecurrent = (allowablepower / voltage) * 1000U;
/* Choose the best PDO depending on the user preferences */
switch (Method)
{
case PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_PWR:
if (allowablepower > selpower)
{
/* Consider the current PDO the best one until now */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
break;
case PDO_SEL_METHOD_MIN_PWR:
if ((allowablepower < selpower) || (selpower == 0))
{
/* Consider the current PDO the best one until now */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
break;
case PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_VOLT:
if (voltage > reqvoltage)
{
/* Consider the current PDO the best one until now */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
break;
case PDO_SEL_METHOD_MIN_VOLT:
if ((voltage < reqvoltage) || (reqvoltage == 0))
{
/* Consider the current PDO the best one until now */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
break;
case PDO_SEL_METHOD_MAX_CUR:
if (allowablecurrent > selcurrent)
{
/* Consider the current PDO the best one until now */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
break;
case PDO_SEL_METHOD_MIN_CUR:
if ((allowablecurrent < selcurrent) || (selcurrent == 0))
{
/* Consider the current PDO the best one until now */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
break;
default:
/* Default behavior: last PDO is selected */
curr_index = temp_index;
selpower = allowablepower;
reqvoltage = voltage;
selcurrent = allowablecurrent;
}
}
}
/* If a suitable PDO was found */
if (curr_index != DPM_NO_SRC_PDO_FOUND)
{
/* Fill the request power details */
PtrRequestPowerDetails->MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits;
PtrRequestPowerDetails->OperatingCurrentInmAunits = (1000U * selpower) / reqvoltage;
PtrRequestPowerDetails->MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits;
PtrRequestPowerDetails->OperatingPowerInmWunits = selpower;
PtrRequestPowerDetails->RequestedVoltageInmVunits = reqvoltage;
}
return curr_index;
}
/**
* @brief Build RDO to be used in Request message according to selected PDO from received SRC Capabilities
* @param PortNum Port number
* @param IndexSrcPDO Index on the selected SRC PDO (value between 0 to 6)
* @param PtrRequestPowerDetails Sink requested power details structure pointer
* @param Rdo Pointer on the RDO
* @param PtrPowerObject Pointer on the selected power object
* @retval None
*/
void DPM_SNK_BuildRDOfromSelectedPDO(uint8_t PortNum, uint8_t IndexSrcPDO,
USBPD_DPM_SNKPowerRequestDetails_TypeDef *PtrRequestPowerDetails,
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef* Rdo, USBPD_CORE_PDO_Type_TypeDef *PtrPowerObject)
{
uint32_t mv = 0, mw = 0, ma = 0, size;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef rdo;
USBPD_HandleTypeDef *pdhandle = &DPM_Ports[PortNum];
USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *puser = (USBPD_USER_SettingsTypeDef *)&DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum];
uint32_t snkpdolist[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO];
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef snk_fixed_pdo;
/* Initialize RDO */
rdo.d32 = 0;
/* Read SNK PDO list for retrieving useful data to fill in RDO */
USBPD_PWR_IF_GetPortPDOs(PortNum, USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SNK_PDO, (uint8_t*)&snkpdolist[0], &size);
/* Store value of 1st SNK PDO (Fixed) in local variable */
snk_fixed_pdo.d32 = snkpdolist[0];
/* Set common fields in RDO */
pdo.d32 = pdhandle->DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[0];
rdo.GenericRDO.USBCommunicationsCapable = snk_fixed_pdo.SNKFixedPDO.USBCommunicationsCapable;
if (USBPD_SPECIFICATION_REV2 < DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_SpecRevision)
{
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.UnchunkedExtendedMessage = DPM_Settings[PortNum].PE_PD3_Support.d.PE_UnchunkSupport;
DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_UnchunkSupport = USBPD_FALSE;
/* Set unchuncked bit if supported by port partner;*/
if (USBPD_TRUE == pdo.SRCFixedPDO.UnchunkedExtendedMessage)
{
DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_UnchunkSupport = USBPD_TRUE;
}
}
/* If no valid SNK PDO or if no SRC PDO match found (index>=nb of valid received SRC PDOs */
if ((size < 1) || (IndexSrcPDO >= pdhandle->DPM_NumberOfRcvSRCPDO))
{
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateCapabilities: Mismatch, could not find desired pdo index */
#ifdef _TRACE
USBPD_TRACE_Add(USBPD_TRACE_DEBUG, PortNum, 0, (uint8_t *)"DPM_SNK_BuildRDOfromSelectedPDO: Pb in SRC PDO selection",
sizeof("DPM_SNK_BuildRDOfromSelectedPDO: Pb in SRC PDO selection"));
#endif /* _TRACE */
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.ObjectPosition = 1;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.OperatingCurrentIn10mAunits = pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.MaxOperatingCurrent10mAunits = pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.CapabilityMismatch = 1;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.USBCommunicationsCapable = snk_fixed_pdo.SNKFixedPDO.USBCommunicationsCapable;
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedCurrent = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits;
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateCapabilities: Mismatch, could not find desired pdo index */
pdhandle->DPM_RequestDOMsg = rdo.d32;
return;
}
/* Set the Object position */
rdo.GenericRDO.ObjectPosition = IndexSrcPDO + 1;
rdo.GenericRDO.NoUSBSuspend = 0;
/* Extract power information from Power Data Object */
pdo.d32 = pdhandle->DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[IndexSrcPDO];
*PtrPowerObject = pdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject;
/* Retrieve request details from SRC PDO selection */
mv = PtrRequestPowerDetails->RequestedVoltageInmVunits;
ma = PtrRequestPowerDetails->OperatingCurrentInmAunits;
switch(pdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED:
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE:
{
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateCapabilities: Mismatch, less power offered than the operating power */
ma = USBPD_MIN(ma, puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits);
mw = (ma * mv)/1000; /* mW */
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedCurrent = ma;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.OperatingCurrentIn10mAunits = ma / 10;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.MaxOperatingCurrent10mAunits = ma / 10;
if(mw < puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.OperatingPowerInmWunits)
{
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateCapabilities: Mismatch, less power offered than the operating power */
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.MaxOperatingCurrent10mAunits = puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits / 10;
rdo.FixedVariableRDO.CapabilityMismatch = 1;
}
}
break;
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY:
{
/* USBPD_DPM_EvaluateCapabilities: Battery Request Data Object */
mw = USBPD_MIN(PtrRequestPowerDetails->OperatingPowerInmWunits, puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits); /* mW */
ma = (1000 * mw) / mv; /* mA */
ma = USBPD_MIN(ma, puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits);
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedCurrent = ma;
mw = (ma * mv)/1000; /* mW */
rdo.BatteryRDO.OperatingPowerIn250mWunits = mw / 250;
rdo.BatteryRDO.MaxOperatingPowerIn250mWunits = mw / 250;
if(mw < puser->DPM_SNKRequestedPower.OperatingPowerInmWunits)
{
/* Mismatch, less power offered than the operating power */
rdo.BatteryRDO.CapabilityMismatch = 1;
}
}
break;
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO:
{
DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestedCurrent = ma;
rdo.ProgRDO.ObjectPosition = IndexSrcPDO + 1;
rdo.ProgRDO.OperatingCurrentIn50mAunits = ma / 50;
rdo.ProgRDO.OutputVoltageIn20mV = mv / 20;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
pdhandle->DPM_RequestDOMsg = rdo.d32;
pdhandle->DPM_RDOPosition = rdo.GenericRDO.ObjectPosition;
Rdo->d32 = pdhandle->DPM_RequestDOMsg;
/* Get the requested voltage */
pdhandle->DPM_RequestedVoltage = mv;
}
/**
* @brief Turn Off power supply.
* @param PortNum The current port number
* @param Role Port power role
* @retval USBPD_OK, USBPD_ERROR
*/
static USBPD_StatusTypeDef DPM_TurnOffPower(uint8_t PortNum, USBPD_PortPowerRole_TypeDef Role)
{
USBPD_StatusTypeDef status;
status = USBPD_PWR_IF_VBUSDisable(PortNum);
return status;
}
/**
* @brief Turn On power supply.
* @param PortNum The current port number
* @param Role Port power role
* @retval USBPD_ACCEPT, USBPD_WAIT, USBPD_REJECT
*/
static USBPD_StatusTypeDef DPM_TurnOnPower(uint8_t PortNum, USBPD_PortPowerRole_TypeDef Role)
{
USBPD_StatusTypeDef status;
/* Enable the output */
status = USBPD_PWR_IF_VBUSEnable(PortNum);
if (USBPD_PORTPOWERROLE_SRC == Role)
{
/* Enable the output */
USBPD_DPM_WaitForTime(20);
}
else
{
/* stop current sink */
}
return status;
}
/**
* @brief Assert Rp resistor.
* @param PortNum The current port number
* @retval None
*/
static void DPM_AssertRp(uint8_t PortNum)
{
USBPD_CAD_AssertRp(PortNum);
}
/**
* @brief Assert Rd resistor.
* @param PortNum The current port number
* @retval None
*/
static void DPM_AssertRd(uint8_t PortNum)
{
USBPD_CAD_AssertRd(PortNum);
}
|
| usbpd_pdo_defs.h |
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Typedef */ tags:
/**
* @brief USBPD Port PDO Structure definition
*/
typedef struct
{
uint32_t *ListOfPDO; /*!< Pointer on Power Data Objects list, defining port capabilities */
uint8_t *NumberOfPDO; /*!< Number of Power Data Objects defined in ListOfPDO
This parameter must be set at max to @ref USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO value */
} USBPD_PortPDO_TypeDef;
/**
* @brief USBPD Port PDO Storage Structure definition
*/
typedef struct
{
USBPD_PortPDO_TypeDef SourcePDO; /*!< SRC Power Data Objects */
USBPD_PortPDO_TypeDef SinkPDO; /*!< SNK Power Data Objects */
} USBPD_PWR_Port_PDO_Storage_TypeDef;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Variables */ tags: #ifndef _GUI_INTERFACE
#ifndef __USBPD_PWR_IF_C
extern uint8_t USBPD_NbPDO[4];
extern uint32_t PORT0_PDO_ListSRC[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO];
extern uint32_t PORT0_PDO_ListSNK[USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO];
#else /* __USBPD_PWR_IF_C */
uint8_t USBPD_NbPDO[4] = {(PORT0_NB_SINKPDO),
(PORT0_NB_SOURCEPDO)};
#endif /* __USBPD_PWR_IF_C */
#endif /* _GUI_INTERFACE */
|
| usbpd_pwr_if.c |
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Private_Defines */ tags:
#if ((PORT0_NB_SINKPDO+PORT0_NB_SINKAPDO) > USBPD_MAX_NB_PDO)
#error "Nb of Sink PDO/APDO is exceeding stack capabilities"
#endif
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Private_Macro */ tags: #define _PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MIN(_PDO_VOLT_, _SNK_VOLT_) \
if ((_PDO_VOLT_) < (_SNK_VOLT_)) \
{ \
/* Update min voltage */ \
(_SNK_VOLT_) = (_PDO_VOLT_); \
}
#define _PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MAX(_PDO_VOLT_, _SNK_VOLT_) \
if ((_PDO_VOLT_) > (_SNK_VOLT_)) \
{ \
/* Update min voltage */ \
(_SNK_VOLT_) = (_PDO_VOLT_); \
}
#define _PWR_UPDATE_CURRENT_MAX(_PDO_CURRENT_, _SNK_CURRENT_) \
if ((_PDO_CURRENT_) > (_SNK_CURRENT_)) \
{ \
/* Update min current */ \
(_SNK_CURRENT_) = (_PDO_CURRENT_); \
}
#define _PWR_UPDATE_POWER_MAX(_PDO_POWER_, _SNK_POWER_) \
if ((_PDO_POWER_) > (_SNK_POWER_)) \
{ \
/* Update min POWER */ \
(_SNK_POWER_) = (_PDO_POWER_); \
}
#if defined(_GUI_INTERFACE)
#define _PWR_CHECK_VOLTAGE_MIN(_PDO_VOLT_, _SNK_VOLT_) \
/* Update min voltage */ \
(_SNK_VOLT_) = (_PDO_VOLT_);
#define _PWR_CHECK_VOLTAGE_MAX(_PDO_VOLT_, _SNK_VOLT_) \
/* Update min voltage */ \
(_SNK_VOLT_) = (_PDO_VOLT_);
#define _PWR_CHECK_CURRENT_MAX(_PDO_CURRENT_, _SNK_CURRENT_) \
/* Update min current */ \
(_SNK_CURRENT_) = (_PDO_CURRENT_);
#define _PWR_CHECK_POWER_MAX(_PDO_POWER_, _SNK_POWER_) \
/* Update min POWER */ \
(_SNK_POWER_) = (_PDO_POWER_);
#else
#define _PWR_CHECK_VOLTAGE_MIN(_PDO_VOLT_, _SNK_VOLT_) \
if ((_PDO_VOLT_) != (_SNK_VOLT_)) \
{ \
/* Disalignment between PDO and DPM_SNKRequestedPower structure */ \
_status = USBPD_ERROR; \
}
#define _PWR_CHECK_VOLTAGE_MAX(_PDO_VOLT_, _SNK_VOLT_) \
if ((_PDO_VOLT_) != (_SNK_VOLT_)) \
{ \
/* Disalignment between PDO and DPM_SNKRequestedPower structure */ \
_status = USBPD_ERROR; \
}
#define _PWR_CHECK_CURRENT_MAX(_PDO_CURRENT_, _SNK_CURRENT_) \
if ((_PDO_CURRENT_) != (_SNK_CURRENT_)) \
{ \
/* Disalignment between PDO and DPM_SNKRequestedPower structure */ \
_status = USBPD_ERROR; \
}
#define _PWR_CHECK_POWER_MAX(_PDO_POWER_, _SNK_POWER_) \
if ((_PDO_POWER_) != (_SNK_POWER_)) \
{ \
/* Disalignment between PDO and DPM_SNKRequestedPower structure */ \
_status = USBPD_ERROR; \
}
#endif /* _GUI_INTERFACE */
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END Private_Variables */ tags: uint32_t vbus_disconnect = 0;
uint32_t vbus_transition = 0;
/**
* @brief USBPD Port PDO Storage array declaration
*/
USBPD_PWR_Port_PDO_Storage_TypeDef PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[USBPD_PORT_COUNT];
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_USER_PRIVATE_FUNCTIONS_Prototypes */ tags: USBPD_StatusTypeDef PWR_IF_CheckUpdateSNKPower(uint8_t PortNum);
/* Functions to initialize Source PDOs */
uint32_t _PWR_SRCFixedPDO(float _C_, float _V_,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_PeakCurr_TypeDef _PK_,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRDataSupport_TypeDef DRDSupport,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_USBCommCapable_TypeDef UsbCommCapable,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_ExtPowered_TypeDef ExtPower,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_USBSuspendSupport_TypeDef UsbSuspendSupport,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRPowerSupport_TypeDef DRPSupport);
uint32_t _PWR_SRCVariablePDO(float _MAXV_, float _MINV_, float _C_);
uint32_t _PWR_SRCBatteryPDO(float _MAXV_,float _MINV_,float _PWR_);
/* Functions to initialize Sink PDOs */
uint32_t _PWR_SNKFixedPDO(float _C_, float _V_,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRDataSupport_TypeDef DRDSupport,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_USBCommCapable_TypeDef UsbCommCapable,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_ExtPowered_TypeDef ExtPower,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_HigherCapability_TypeDef HigherCapab,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRPowerSupport_TypeDef DRPSupport);
uint32_t _PWR_SNKVariablePDO(float _MAXV_,float _MINV_,float _C_);
uint32_t _PWR_SNKBatteryPDO(float _MAXV_,float _MINV_,float _PWR_);
uint32_t _PWR_ProgrammablePowerSupplyAPDO(float _MAXC_,float _MINV_,float _MAXV_);
void _PWR_CheckPDOContent(uint8_t PortNum);
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_PWR_IF_Init */ tags: USBPD_StatusTypeDef _status = USBPD_OK;
/* Set links to PDO values and number for Port 0 (defined in PDO arrays in H file). */
PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[USBPD_PORT_0].SourcePDO.ListOfPDO = (uint32_t *) PORT0_PDO_ListSRC;
PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[USBPD_PORT_0].SourcePDO.NumberOfPDO = &USBPD_NbPDO[1];
PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[USBPD_PORT_0].SinkPDO.ListOfPDO = (uint32_t *)PORT0_PDO_ListSNK;
PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[USBPD_PORT_0].SinkPDO.NumberOfPDO = &USBPD_NbPDO[0];
return _status;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_PWR_IF_SetProfile */ tags: USBPD_PDO_TypeDef _pdo;
USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef _rdo;
_rdo.d32 = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RcvRequestDOMsg;
_pdo.d32 = PORT0_PDO_ListSRC[0];
return (BSP_ERROR_NONE == BSP_USBPD_PWR_VBUSSetVoltage_Fixed(PortNum,
_pdo.SRCFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits * 50,
(_rdo.FixedVariableRDO.OperatingCurrentIn10mAunits * 10),
(_rdo.FixedVariableRDO.MaxOperatingCurrent10mAunits * 10)
)? USBPD_OK : USBPD_ERROR);
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_PWR_IF_GetPortPDOs */ tags: if (DataId == USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SRC_PDO)
{
#if defined (_GUI_INTERFACE)
*Size = USBPD_NbPDO[1];
memcpy(Ptr,PORT0_PDO_ListSRC, sizeof(uint32_t) * USBPD_NbPDO[1]);
#else
*Size = PORT0_NB_SOURCEPDO;
memcpy(Ptr,PORT0_PDO_ListSRC, sizeof(uint32_t) * PORT0_NB_SOURCEPDO);
#endif /* _GUI_INTERFACE */
}
else
{
#if defined (_GUI_INTERFACE)
*Size = USBPD_NbPDO[0];
memcpy(Ptr,PORT0_PDO_ListSNK, sizeof(uint32_t) * USBPD_NbPDO[0]);
#else
*Size = PORT0_NB_SINKPDO;
memcpy(Ptr,PORT0_PDO_ListSNK, sizeof(uint32_t) * PORT0_NB_SINKPDO);
#endif /* _GUI_INTERFACE */
}
uint32_t nbpdo, index, nb_valid_pdo = 0;
uint32_t *ptpdoarray = NULL;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo_first;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
/* Check if valid port */
if (USBPD_PORT_IsValid(PortNum))
{
/* According to type of PDO to be read, set pointer on values and nb of elements */
switch (DataId)
{
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SRC_PDO :
nbpdo = *PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SourcePDO.NumberOfPDO;
ptpdoarray = PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SourcePDO.ListOfPDO;
/* Save the 1st PDO */
pdo_first.d32 = *ptpdoarray;
/* Reset unchunked bit if current revision is PD2.0*/
if (USBPD_SPECIFICATION_REV2 == DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_SpecRevision)
{
pdo_first.SRCFixedPDO.UnchunkedExtendedMessage = USBPD_PDO_SRC_FIXED_UNCHUNK_NOT_SUPPORTED;
}
break;
case USBPD_CORE_DATATYPE_SNK_PDO:
nbpdo = *PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SinkPDO.NumberOfPDO;
ptpdoarray = PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SinkPDO.ListOfPDO;
/* Save the 1st PDO */
pdo_first.d32 = *ptpdoarray;
/* Reset FRS bit if current revision is PD2.0*/
if (USBPD_SPECIFICATION_REV2 == DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_SpecRevision)
{
pdo_first.SNKFixedPDO.FastRoleSwapRequiredCurrent = USBPD_PDO_SNK_FIXED_FRS_NOT_SUPPORTED;
}
break;
default:
nbpdo = 0;
break;
}
/* Copy PDO data in output buffer */
for (index = 0; index < nbpdo; index++)
{
pdo.d32 = *ptpdoarray;
/* Copy only PDO (and not APDO in case of current revision is PD2.0) */
if ((USBPD_SPECIFICATION_REV2 == DPM_Params[PortNum].PE_SpecRevision)
&& (pdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject == USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO))
{
}
else
{
/* Copy 1st PDO as potentially FRS or UNCHUNKED bits have been reset */
if (0 == index)
{
(void)memcpy(Ptr, (uint8_t*)&pdo_first.d32, 4u);
}
else
{
(void)memcpy((Ptr + (nb_valid_pdo * 4u)), (uint8_t*)ptpdoarray, 4u);
}
nb_valid_pdo++;
}
ptpdoarray++;
}
/* Set nb of read PDO (nb of u32 elements); */
*Size = nb_valid_pdo;
}
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_PWR_IF_SearchRequestedPDO */ tags: if((RdoPosition == 0) || (RdoPosition > *PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SourcePDO.NumberOfPDO))
{
/* Invalid PDO index */
return USBPD_FAIL;
}
*Pdo = PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SourcePDO.ListOfPDO[RdoPosition - 1];
return USBPD_OK;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_PWR_IF_UpdateVbusThreshold */ tags: USBPD_SNKRDO_TypeDef rdo; /* get the requested RDO */
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef SelectedPDO;
rdo.d32 = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_RequestDOMsg;
SelectedPDO.d32 = DPM_Ports[PortNum].DPM_ListOfRcvSRCPDO[rdo.GenericRDO.ObjectPosition - 1];
switch (SelectedPDO.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED :
{
switch (SelectedPDO.SRCFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits * 50)
{
case 5000 :
vbus_transition = USBPD_PWR_VBUS_THRESHOLD_5V;
break;
case 9000 :
vbus_transition = USBPD_PWR_VBUS_THRESHOLD_9V;
break;
case 15000 :
vbus_transition = USBPD_PWR_VBUS_THRESHOLD_15V;
break;
case 20000 :
vbus_transition = USBPD_PWR_VBUS_THRESHOLD_20V;
break;
}
break;
}
#if defined(USBPD_REV30_SUPPORT) && defined(USBPDCORE_PPS)
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO :
{
vbus_transition = USBPD_PWR_VBUS_THRESHOLD_APDO;
break;
}
#endif /*_USBPD_REV30_SUPPORT && PPS*/
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY :
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE :
{
/* Not yet handled */
break;
}
}
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_PWR_IF_ResetVbusThreshold */ tags: PWR_IF_DEBUG_TRACE(PortNum, "RESET THRESHOLD");
vbus_disconnect = vbus_transition = USBPD_PWR_HIGH_VBUS_THRESHOLD;
Between the /* USER CODE BEGIN-END USBPD_USER_PRIVATE_FUNCTIONS_Definition */ tags: /**
* @brief Function to check validity between SNK PDO and power user settings
* @param PortNum Port number
* @retval USBPD Status
*/
USBPD_StatusTypeDef PWR_IF_CheckUpdateSNKPower(uint8_t PortNum)
{
USBPD_StatusTypeDef _status = USBPD_OK;
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
uint32_t _max_power = 0;
uint16_t _voltage = 0, _current = 0, _power = 0;
uint16_t _min_voltage = 0xFFFF, _max_voltage = 0, _max_current = 0;
for (uint32_t _index = 0; _index < *PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SinkPDO.NumberOfPDO; _index++)
{
pdo.d32 = PWR_Port_PDO_Storage[PortNum].SinkPDO.ListOfPDO[_index];
switch (pdo.GenericPDO.PowerObject)
{
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED: /*!< Fixed Supply PDO */
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_50MV(pdo.SNKFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MIN(_voltage, _min_voltage);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MAX(_voltage, _max_voltage);
_current = PWR_DECODE_10MA(pdo.SNKFixedPDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_CURRENT_MAX(_current, _max_current);
break;
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY: /*!< Battery Supply PDO */
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_50MV(pdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MIN(_voltage, _min_voltage);
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_50MV(pdo.SNKBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MAX(_voltage, _max_voltage);
_power = PWR_DECODE_MW(pdo.SNKBatteryPDO.OperationalPowerIn250mWunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_POWER_MAX(_power, _max_power);
break;
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE: /*!< Variable Supply (non-battery) PDO */
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_50MV(pdo.SNKVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MIN(_voltage, _min_voltage);
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_50MV(pdo.SNKVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MAX(_voltage, _max_voltage);
_current = PWR_DECODE_10MA(pdo.SNKVariablePDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_CURRENT_MAX(_current, _max_current);
break;
case USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO: /*!< Augmented Power Data Object (APDO) */
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_100MV(pdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MinVoltageIn100mV);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MIN(_voltage, _min_voltage);
_voltage = PWR_DECODE_100MV(pdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxVoltageIn100mV);
_PWR_UPDATE_VOLTAGE_MAX(_voltage, _max_voltage);
_current = PWR_DECODE_50MA(pdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxCurrentIn50mAunits);
_PWR_UPDATE_CURRENT_MAX(_current, _max_current);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
_PWR_CHECK_VOLTAGE_MIN(_min_voltage, DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum].DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MinOperatingVoltageInmVunits);
_PWR_CHECK_VOLTAGE_MAX(_max_voltage, DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum].DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingVoltageInmVunits);
_PWR_CHECK_CURRENT_MAX(_max_current, DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum].DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingCurrentInmAunits);
_max_power = (_max_voltage * _max_current) / 1000;
_PWR_CHECK_POWER_MAX(_max_power, DPM_USER_Settings[PortNum].DPM_SNKRequestedPower.MaxOperatingPowerInmWunits);
return _status;
}
/**
* @brief Create SRC Fixed PDO object
* @param _C_: Current in A
* @param _V_: voltage in V
* @param _PK_: The peak of current
* @param DRDSupport: Data Role Swap support indication
* @param UsbCommCapable: USB communications capability indication
* @param ExtPower: Port externally powered indication
* @param UsbSuspendSupport: USB Suspend support indication
* @param DRPSupport: Dual Role Power support indication
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_SRCFixedPDO(float _C_, float _V_,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_PeakCurr_TypeDef _PK_,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRDataSupport_TypeDef DRDSupport,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_USBCommCapable_TypeDef UsbCommCapable,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_ExtPowered_TypeDef ExtPower,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_USBSuspendSupport_TypeDef UsbSuspendSupport,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRPowerSupport_TypeDef DRPSupport)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
pdo.d32 = 0;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits = PWR_A_10MA(_C_);
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_V_);
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.PeakCurrent = _PK_;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.DataRoleSwap = DRDSupport;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.USBCommunicationsCapable = UsbCommCapable;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.ExternallyPowered = ExtPower;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.USBSuspendSupported = UsbSuspendSupport;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.DualRolePower = DRPSupport;
pdo.SRCFixedPDO.FixedSupply = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED;
return pdo.d32;
}
/**
* @brief Create SRC Variable PDO object
* @param _MAXV_ Max voltage in V
* @param _MINV_ Min voltage in V
* @param _C_: Max current in A
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_SRCVariablePDO(float _MAXV_, float _MINV_, float _C_)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
pdo.d32 = 0;
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits = PWR_A_10MA(_C_);
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MAXV_);
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MINV_);
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.VariableSupply = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE;
return pdo.d32;
}
/**
* @brief Create SRC Battery PDO object
* @param _MAXV_ Max voltage in V
* @param _MINV_ Min voltage in V
* @param _PWR_ Max allowable power in W
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_SRCBatteryPDO(float _MAXV_,float _MINV_,float _PWR_)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
pdo.d32 = 0;
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MaxAllowablePowerIn250mWunits = PWR_W(_PWR_);
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MINV_);
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MAXV_);
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.Battery = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY;
return pdo.d32;
}
/**
* @brief Create SNK Fixed PDO object
* @param _C_ Current in A
* @param _V_ voltage in V
* @param DRDSupport: Data Role Swap support indication
* @param UsbCommCapable: USB communications capability indication
* @param ExtPower: Port externally powered indication
* @param HigherCapab: Sink needs more than vSafe5V to provide full functionality indication
* @param DRPSupport: Dual Role Power support indication
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_SNKFixedPDO(float _C_, float _V_,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRDataSupport_TypeDef DRDSupport,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_USBCommCapable_TypeDef UsbCommCapable,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_ExtPowered_TypeDef ExtPower,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_HigherCapability_TypeDef HigherCapab,
USBPD_CORE_PDO_DRPowerSupport_TypeDef DRPSupport)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
pdo.d32 = 0;
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.OperationalCurrentIn10mAunits = PWR_A_10MA(_C_);
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.VoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_V_);
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.DataRoleSwap = DRDSupport;
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.USBCommunicationsCapable = UsbCommCapable;
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.ExternallyPowered = ExtPower;
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.HigherCapability = HigherCapab;
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.DualRolePower = DRPSupport;
pdo.SNKFixedPDO.FixedSupply = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_FIXED;
return pdo.d32;
}
/**
* @brief Create SNK Variable PDO object
* @param _MAXV_ Max voltage in V
* @param _MINV_ Min voltage in V
* @param _C_: Max current in A
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_SNKVariablePDO(float _MAXV_,float _MINV_,float _C_)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
pdo.d32 = 0;
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.MaxCurrentIn10mAunits = PWR_A_10MA(_C_);
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MAXV_);
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MINV_);
pdo.SRCVariablePDO.VariableSupply = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_VARIABLE;
return pdo.d32;
}
/**
* @brief Create SNK Battery PDO object
* @param _MAXV_ Max voltage in V
* @param _MINV_ Min voltage in V
* @param _PWR_ Max allowable power in W
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_SNKBatteryPDO(float _MAXV_,float _MINV_,float _PWR_)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef pdo;
pdo.d32 = 0;
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MaxAllowablePowerIn250mWunits = PWR_W(_PWR_);
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MinVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MINV_);
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.MaxVoltageIn50mVunits = PWR_V_50MV(_MAXV_);
pdo.SRCBatteryPDO.Battery = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_BATTERY;
return pdo.d32;
}
#if _PPS
/**
* @brief Create Programmable Power Supply APDO object
* @param _MAXC_ Max Current in A
* @param _MINV_ Min voltage in V
* @param _MAXV_ Max voltage in V
* @retval PDO object value (expressed on u32)
*/
uint32_t _PWR_ProgrammablePowerSupplyAPDO(float _MAXC_,float _MINV_,float _MAXV_)
{
USBPD_PDO_TypeDef apdo;
apdo.d32 = 0;
apdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxCurrentIn50mAunits = PWR_A_50MA(_MAXC_); /*!< Maximum Current in 50mA increments */
apdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MinVoltageIn100mV = PWR_V_100MV(_MINV_); /*!< Minimum Voltage in 100mV increments */
apdo.SRCSNKAPDO.MaxVoltageIn100mV = PWR_V_100MV(_MAXV_); /*!< Maximum Voltage in 100mV increments */
apdo.SRCSNKAPDO.PPS_APDO = USBPD_CORE_PDO_TYPE_APDO;
return apdo.d32;
}
#endif /* _PPS */
|
10. Project with a custom board
This chapter describes how to build a USB PD source application using a custom board with an STM32 MCU from series G0, G4, H5, L5, or U5 that includes the UCPD peripheral.
- As in the chapter 2, create the project.
- As in the chapter 3.1, clear the pinout.
- As per chapter 3.2, select the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack.
But do not select the board support for X-NUCLEO-SRC1M1 as your application is based on a custom board.
- As in the chapter 3.3, configure the UCPD peripheral.
- As in the chapter 3.4, configure the FreeRTOS™ middleware.
- As in the chapter 3.5, configure the USB PD middleware.
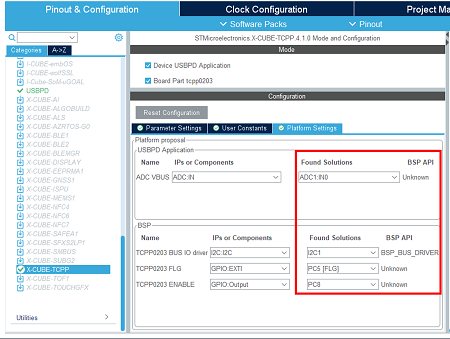
- Configure the ADC peripheral.
Select and configure the ADC and its channel on which Vbus is connected for monitoring. Select the ADC and it channel. Adjust the clock prescaler. Keep the 12-bits resolution. Enable the continuous conversion mode. Set a medium cycle sampling time.
- Configure the I2C peripheral.
Enable the I2C connected to the TCPP02 I2C bus. Set its speed in fast mode.
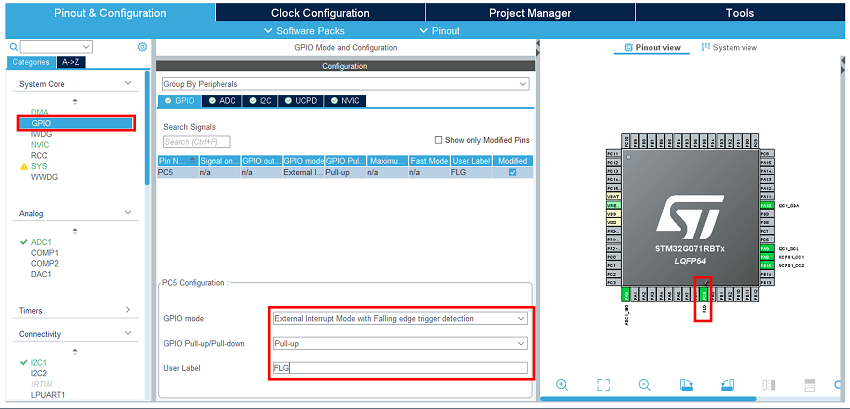
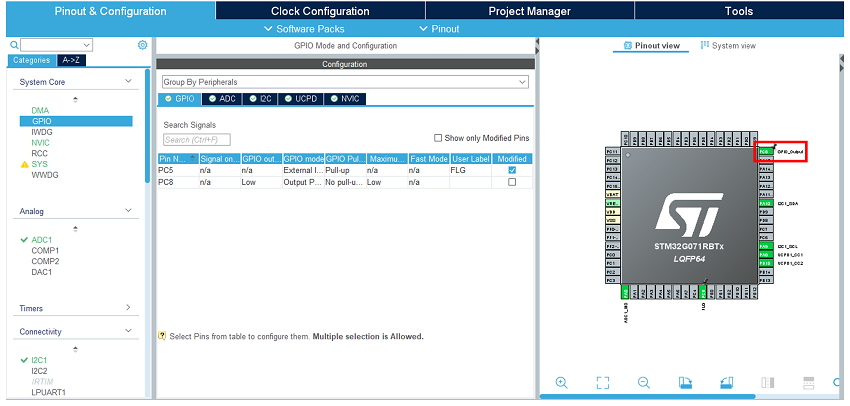
- Configure the GPIO.
Enable and configure the external interrupt input where the TCPP02 FLG signal is connected. Select it in the pinout view. In the GPIO category, set it as external interrupt mode with falling edge trigger detection. Enable its pull-up.
In the pinout view, select the GPIO output for TCPP02 enable.
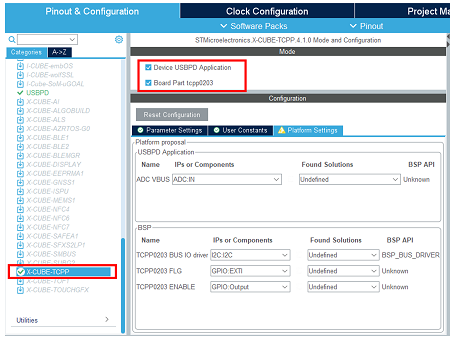
- Enable the software pack.
In the middleware category, select the X-CUBE-TCPP software pack and enable its application and Board part.
- Assign resources to the application requirements.
- As in the chapter 4, configure the project.
But in the advanced settings keep ADC and I2C initialization code generation.
- As in the chapter 5, generate the code.
- As in the chapter 7, compile and run the application.
11. References