1. Introduction
The Bluetooth® LE Audio Content Control section regroups:
- The Call Control Profile (CCP)
- The Generic Telephony Bearer Service (GTBS)
- The Telephony Bearer Service (TBS)
- The Media Control Profile (MCP)
- The Generic Media Control Service (GMCS)
- The Media Control Service (MCS)
These profiles and services are used to either control or provide status information on Call features and Media features.
|
Figure 1.1 STM32WBA Bluetooth® Low Energy - Content Control |
As specified in section 2.2 of the Common Audio Profile[1], the CAP Acceptor or the CAP Commander can operate in the MCP Client role and the CCP Client role, and the CAP Initiator can operate in the CCP Server role and the MCP Server role.
The GTBS, the TBS, the GMCS and the MCS are defined as Content Control services.
2. Call Control Profile
The Call Control profile defines roles and procedures to handle call control for bearers on device that can make and receive phone calls. It is specified by the Bluetooth® SIG and the full specification is accessible on their website[2].
2.1. Roles
The CCP introduces two roles:
- Call Control Server: handles calls on one or more telephone call bearers. This role can be used by cell phones or tablets.
- Call Control Client: makes requests to the server to make, receive, and manage calls. This role can be used by a headset or a speaker with microphones, or by devices such as a watch that might not have a speaker or microphone but can manage telephony calls.
The section Bluetooth® Low Energy audio stack configuration of this wiki article[3] describes how to configure and initialize the CCP role and to allocate required ROM, RAM and GATT resources.
2.2. Telephone Bearer
Within a Call Control Server, there can be zero or multiple instances of Telephone Bearer Service (TBS), and there is a single mandatory instance of Generic Telephone Bearer Service. Each of them describes a single Telephone Bearer instance.
A Call Control Server can implement multiple Telephone Bearer instances, allowing a Call Control Client to access separate internal telephone bearer entities, such as various end-user applications (for example, cellular call and VoIP applications).
The Bluetooth® LE audio stack provides two APIs declared incap.h header file to register the Telephony Bearer instance associated to the Telephone Bearer Service and the Generic Telephone Bearer Service (refer to table 2.1).
| Functions | Description | Header File |
|---|---|---|
| CAP_RegisterGenericTelephonyBearer() | Register the Generic Telephone Bearer. | cap.h |
| CAP_RegisterTelephonyBearerInstance() | Register the Telephone Instance. | cap.h |
If the Call Feature is supported, the CAP_RegisterGenericTelephonyBearer() function shall be called (mandatory to expose a Generic Telephone Bearer) and the CAP_RegisterTelephonyBearerInstance() function can be called according to the number of separate bearer instances.
Each registered Telephony Bearer instance is identified by a unique identifier value named Content Control Identifier (CCID). The CCID value identifies a Content Control service (GTBS or TBS) and is unique for that service instance across all instances of Content Control services on a device.
2.3. Call Control Profile Linkup
The linkup operation of the Call Control Profile can be initialized by the CAP Acceptor or the CAP Commander supporting the Call Control Client role using the CAP_Linkup() function. This process is described in section 4.1 Audio profiles linkup of this wiki article[3].
During the linkup of the Call Control Profile, the CCP META event CCP_CLT_GTBS_INFO_EVT and CCP_CLT_TBS_INFO_EVT are reported in CAP Callback when Generic Telephone Bearer Service and Telephony Bearer Service instances are discovered in remote CAP Initiator supporting CCP Server role.
Once the Call Control Profile link is up, the CAP_CCP_LINKUP_EVT event is notified.
2.4. Call Control Profile Functions
All the Call Control Profile functions defined in the header file ccp.h are used to control the Call features in CCP Server and CCP Client roles.
All the structures, types, callback events related to the Call Control feature are defined in the ccp_types.h header file.
2.4.1. Call State Management
The Call Control Client and the Call Control Server support functions dedicated to managing call state transition.
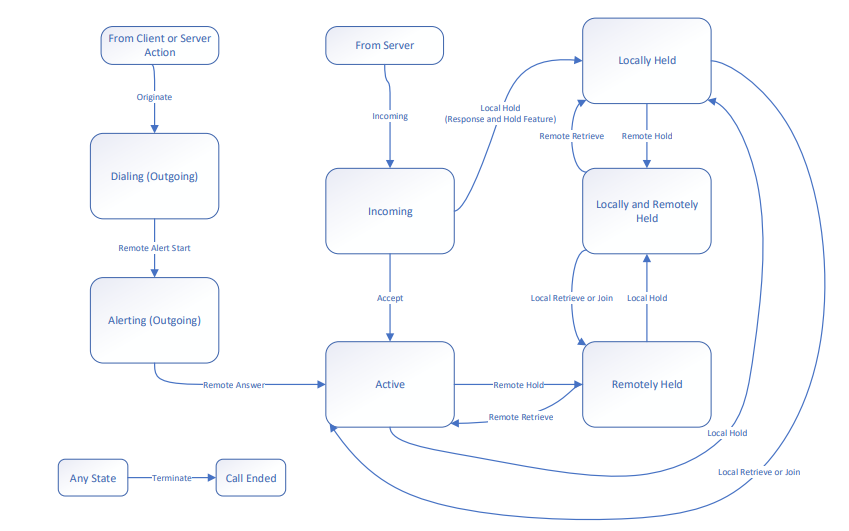
The Telephone Bearer Service Specification[4] describes the Call State Transition represented by the following figure:
|
Figure 2.1 STM32WBA Bluetooth® Low Energy - Call State Machine |
Table 2.2 lists the Call Control functions supported by the Call Control Server.
When the state of a Call changes in Call Control Server role, the CCP META Event CCP_SRV_CALL_STATE_EVT is notified.
| Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| CCP_SERVER_SetupIncomingCall() | Set up an incoming call. Can be associated to the CCP_SERVER_SetIncomingCallTargetURI() function used to set the Incoming Call Target Bearer URI of the incoming call. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetupOutgoingCall() | Set up an outgoing call.
Could be associated to the CCP_SERVER_SetCallFriendlyName() function used to set the Call Friendly Name of the outgoing call. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetAlertingCall() | Set an outgoing call in alerting state. |
| CCP_SERVER_TerminateCall() | Terminate a call. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetActiveCall() | Set a call in active state. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetLocalHoldCall() | Place a call in locally held state. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetRemoteHoldCall() | Place a call in remotely held state. |
| CCP_SERVER_RetrieveCall() | Retrieve a call in locally held or locally and remotely held state. |
| CCP_SERVER_JoinCalls() | Join multiple calls in active state. |
Table 2.3 lists the Call Control functions supported by the Call Control Client. Once associated operation is transmitted, the CCP META Event CCP_CLT_OPERATION_TRANSMITTED_EVT is notified.
When the state of a Call changes in Call Control Client role, the CCP META Event CCP_CLT_CALL_STATE_EVT is notified.
| Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| CCP_CLIENT_AnswerIncomingCall() | Answer an incoming call. |
| CCP_CLIENT_TerminateCall() | End an active, alerting (outgoing), dialing (outgoing), incoming, or held (locally or remotely) call. |
| CCP_CLIENT_LocalHoldCall() | Place an active or incoming call on local hold.
Place a remotely held call on locally and remotely hold. |
| CCP_CLIENT_ActivateLocalHeldCall() | Move a call that is being locally held to an active call. |
| CCP_CLIENT_RetrieveLocallyAndRemotelyHeldCall() | Move a call that is being locally and remotely held to a remotely held call. |
| CCP_CLIENT_OriginateCall() | Make an outgoing call. |
| CCP_CLIENT_JoinCalls() | Join multiple calls. |
Note that each function listed above manages the state transition of a call associated to a specific Content Control ID of a Telephone Bearer Instance.
2.4.2. Telephone Bearer Information
The Call Control Client and the Call Control Server support functions dedicated to set (server) and get (client) information related to a specific Telephone Bearer instance.
Table 2.4 lists the Call Control functions supported by the Call Control Server.
| Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| CCP_SERVER_SetProviderName() | Set the Telephone Bearer Provider Name. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetBearerTechnology() | Set the Telephone Bearer Technology. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetURISchemesSupportedList() | Set the list of the supported URI schemes. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetBearerSignalStrength() | Set the current signal strength. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetFeaturesStatus() | Set the current status of features supported by the driver. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetCallControlOptions() | Set the Call Control Options supported or not by the CCP Server. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetIncomingCallTargetURI() | Set the Incoming Call Target Bearer URI. |
| CCP_SERVER_SetCallFriendlyName() | Set the call friendly name. |
Table 2.5 lists the Call Control functions supported by the Call Control Client and the CCP_META events notified when response is received from the remote CCP Server. Once the associated operation is transmitted to the remote CCP Server, the CCP_META event CCP_CLT_OPERATION_COMPLETE_EVT is notified.
The CCP_CLIENT_ConfigureSignalStrengthNotification() and CCP_CLIENT_ConfigureCurrentCallsListNotification() functions are used by CCP Client to enable/disable the signal strength update notification (CCP_CLT_SIGNAL_STRENGTH_EVT) and the Bearer current calls list update notification (CCP_CLT_CURRENT_CALL_EVT).
| Functions | Description | Event |
|---|---|---|
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadProviderName() | Read the Bearer Provider Name. | CCP_CLT_PROVIDER_NAME_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadUCI() | Read the Bearer Uniform Caller Identifier. | CCP_CLT_UCI_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadTechnology() | Read the Bearer Technology. | CCP_CLT_TECHNOLOGY_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadSupportedURISchemesList() | Read the Bearer URI Schemes supported list. | CCP_CLT_URI_SCHEMES_LIST_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadSignalStrength() | Read the Bearer signal strength. | CCP_CLT_SIGNAL_STRENGTH_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadSSRInterval() | Read the Bearer Signal strength reporting interval. | CCP_CLT_SSR_INTERVAL_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_SetSSRInterval() | Set the Bearer signal strength reporting interval. No CCP_CLT_OPERATION_COMPLETE_EVT is notified for this function. |
|
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadListCurrentCalls() | Read the Bearer List current calls. | CCP_CLT_CURRENT_CALL_EVT CCP_CLT_NO_CURRENT_CALL_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadIncomingCallTargetURI() | Read the Incoming Call Target Bearer URI. | CCP_CLT_INC_CALL_TARGET_URI_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadFeaturesStatus() | Read the feature (inband ring tone and silent mode) status. | CCP_CLT_FEATURES_STATUS_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadCallState() | Read the various states of telephone calls. | CCP_CLT_CALL_STATE_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadCallCtrlOptions() | Read the call control point optional opcodes. | CCP_CLT_CALL_CTRL_OPTIONS_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadIncomingCall() | Read the incoming call. | CCP_CLT_INCOMING_CALL_EVT |
| CCP_CLIENT_ReadCallFriendlyName() | Read the call friendly name. | CCP_CLT_CALL_FRIENDLY_NAME_EVT |
3. Media Control Profile
The Media Control profile defines roles and procedures to handle media control and status of Media Playback entities on device. It is specified by the Bluetooth® SIG and the full specification is accessible on their website[5].
3.1. Roles
The MCP introduces two roles:
- Media Control Server: interacts with a Media Control Client for the management of media tracks and conveys various states and settings to the Media Control Client. This role can be used by cell phones or tablets.
- Media Control Client: initiates playing and pausing, determines playing order, and collects search results from the Media Control Server. This role can be used by a headset or a speaker.
The section Bluetooth® Low Energy audio stack configuration of this wiki article[3] describes how to configure and initialize the MCP role and to allocate required ROM, RAM and GATT resources.
3.2. Media Player
Within a Media Control Server, there can be zero or multiple instances of Media Control Service (MCS), and there is a single mandatory instance of Generic Media Control Service (GMCS). Each of them describes a single Media Player.
A Media Control Server can implement multiple Media Player instances, allowing a Media Control Client to access separate internal media player entities, such as various end-user applications playing music on a phone or a computer.
The Bluetooth® LE audio stack provides two APIs declared incap.h header file to register the Media Player instance associated to the Media Control Service and the Generic Media Control Service (refer to Table 3.1).
| Functions | Description | Header File |
|---|---|---|
| CAP_RegisterGenericMediaPlayer() | Register the Generic Media Player. | cap.h |
| CAP_RegisterMediaPlayerInstance() | Register the Media Player Instance. | cap.h |
If the Media Feature is supported, the CAP_RegisterGenericMediaPlayer() function shall be called (mandatory to expose a Generic Media Player) and the CAP_RegisterMediaPlayerInstance() function can be called according to the number of separate media instances.
Each registered Media Player instance is identified by a unique identifier value named Content Control Identifier (CCID).The CCID value identifies a Content Control service (GMCS or MCS) and is unique for that service instance across all instances of Content Control services on a device.
3.3. Media Control Profile Linkup
The linkup operation of the Media Control Profile can be initialized by the CAP Acceptor or the CAP Commander supporting the Media Control Client role using the CAP_Linkup() function. This process is described in section 4.1 Audio profiles linkup of this wiki article[3].
During the linkup of the Media Control Profile, the MCP META Event MCP_CLT_GMP_INFO_EVT and MCP_CLT_MPI_INFO_EVT are reported in CAP Callback when Generic Media Service and Media Service Instances are discovered in remote CAP Initiator supporting MCP Server role.
Once the Media Control Profile link is up, the CAP_MCP_LINKUP_EVT event is notified.
3.4. Media Control Profile Functions
All the Media Control Profile functions defined in the header file mcp.h are used to control the Media features in MCP Server and MCP Client role.
All the structures, types, callback events related to the Media Control feature are defined in the mcp_types.h header file.
3.4.1. Track Management
The Media Control Client and the Media Control Server support functions dedicated to managing operations relative to tracks (track state, track position...).
The Media Control Service Specification[6] defines multiple Media Control operation types, allowing the MCP Client to request the MCP Server to change the track state, the track position, and the current track selection. These operations are defined in MCP_MediaControlOpcode_t type in the mcp_types.h header file.
Each of these Media Control operations can be supported or not by the MCP Server. On the MCP Server side, the MCP_SERVER_SetSupportedMediaCtrlFeatures() allows setting the supported Media Control operations. Onthe MCP Client side, the MCP_CLIENT_ReadMediaCtrlFeatures() allows reading the Media Control operations supported by the peer MCP Server.
On the MCP Server side, the application would be notified with the MCP META event MCP_SRV_CTRL_REQ_EVT when a Media Control operation request is received from a peer MCP Client. The MCP Server must respond to the request using the MCP_SERVER_CtrlOpRsp() function.
Table 3.2 shows MCP Server functions to call when the requested operation is related to the track state, track position or to the current track selection. These functions should be called before responding to the operation request using the MCP_SERVER_CtrlOpRsp() function.
| Media Control Operation | Functions |
|---|---|
| MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_PLAY MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_PAUSE MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_FAST_REWIND MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_FAST_FORWARD MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_STOP |
MCP_SERVER_SetMediaState() |
| MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_MOVE_RELATIVE MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_PREVIOUS_SEGMENT MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_NEXT_SEGMENT MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_FIRST_SEGMENT MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_LAST_SEGMENT MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_GOTO_SEGMENT |
MCP_SERVER_SetTrackPosition() |
| MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_PREVIOUS_TRACK MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_NEXT_TRACK MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_FIRST_TRACK MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_LAST_TRACK MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_GOTO_TRACK MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_PREVIOUS_GROUP MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_NEXT_GROUP MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_FIRST_GROUP MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_LAST_GROUP MCP_MEDIA_CTRL_GOTO_GROUP |
MCP_SERVER_SetTrackTitle() MCP_SERVER_SetTrackDuration() MCP_SERVER_SetTrackPosition() MCP_SERVER_NotifyTrackChanged() |
Table 3.3 lists the Media Control functions supported by the Media Control Client. Once associated operation is transmitted, the MCP META Event MCP_CLT_OPERATION_TRANSMITTED_EVT is notified.
The operation corresponds to a control request transmitted to a peer Media Control Server. The MCP META event MCP_CLT_RESPONSE_EVT is notified once the response of the control request is received from the remote MCP Server.
If some information related to track is updated in the peer MCP Server side, a MCP META event listed in Table 3.3 below is notified.
| Functions | Description | MCP META Event |
|---|---|---|
| MCP_CLIENT_PlayTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to start playing the current track. | MCP_MEDIA_STATE_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_PauseTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to pause the playing current track. | MCP_MEDIA_STATE_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_FastRewindTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to fast rewind the current track. | MCP_MEDIA_STATE_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_FastForwardTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to fast forward the current track. | MCP_MEDIA_STATE_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_StopTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to stop current activity (playing, paused, seeking) and return to the paused state and set the current track position to the start of the current track. | MCP_MEDIA_STATE_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_SetRelativeTrackPosition() | Request the remote MCP Server to set the current track position on the remote MCP Server to a position relative to the current track position. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MovePreviousSegment() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the previous segment within the current track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveNextSegment() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the next segment within the current track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveFirstSegment() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the first segment within the current track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveLastSegment() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the last segment within the current track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveSegmentNumber() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the specified segment within the current track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MovePreviousTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the previous track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveNextTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the next track. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveFirstTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the first track within the current group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveLastTrack() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the last track within the current group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveTrackNumber() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the specified track within the current group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MovePreviousGroup() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the previous group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveNextGroup() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the next group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveFirstGroup() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the first group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveLastGroup() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the last group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_MoveGroupNumber() | Request the remote MCP Server to move to the specified group. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT MCP_CLT_TRACK_CHANGED_EVT |
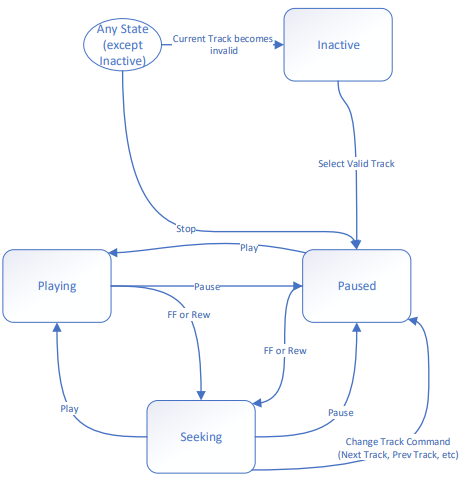
The Media Control Service Specification[6] describes the Media State Transition represented by the following Figure 3.1.
|
Figure 3.1 STM32WBA Bluetooth® Low Energy - Media State Machine |
3.4.2. Media Player settings
The Bluetooth® LE audio stack offers functions in both the MCP Server and MCP Client roles to handle Media Player settings such as the playback speed, the seeking speed, and playing order.
These functions are available in mcp.h header file.
3.4.3. Media Player updates notification configuration
The Bluetooth® LE audio stack offers a variety of functions on the MCP Client side. These functions allow the client to enable or disable notifications of Media Player settings updates from the peer MCP Server.
Table 3.4 lists functions for configuring update notifications and the MCP META event received when a corresponding Media Player setting update is received from a peer device. The MCP META event MCP_CLT_OPERATION_COMPLETE_EVT is notified once the update notification configuration operation is complete.
| Function | Description | MCP META Event |
|---|---|---|
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigureMediaPlayerNameNotification() | Configure the Media Player Name update notification. | MCP_CLT_MEDIA_PLAYER_NAME_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigureTrackTitleNotification() | Configure the track title update notification. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_TITLE_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigureTrackDurationNotification() | Configure the track duration update notification. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_DURATION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigureTrackPositionNotification() | Configure the track position update notification. | MCP_CLT_TRACK_POSITION_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigurePlaybackSpeedNotification() | Configure the playback speed update notification. | MCP_CLT_PLAYBACK_SPEED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigureSeekingSpeedNotification() | Configure the seeking speed update notification. | MCP_CLT_SEEKING_SPEED_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigurePlayingOrderNotification() | Configure the playing order update notification. | MCP_CLT_PLAYING_ORDER_EVT |
| MCP_CLIENT_ConfigureMediaCtrlOpSupportedNotification() | Configure the supported Media Control operations update notification. | MCP_CLT_MEDIA_CTRL_OP_FEATURES_EVT |
4. Content Control procedure
As specified in the Common Audio Profile specification, Content Control service instances (Media and/or Call) can be associated with an audio stream using their CCID values when the audio stream carries content controlled by these Content Control service instances.
To inform a remote CAP Acceptor or CAP Commander that an audio stream is associated with one or more Content Control service instances, the CAP Initiator specifies the corresponding CCIDs in the CCID_List LTV structure in the audio stream metadata.
In unicast procedures, when a remote CAP Initiator indicates that a Media Content Control instance or a Call Content Control instance is activated/deactivated. This indication is made through the metadata associated to an audio stream endpoint in enabling/streaming state. The Bluetooth® LE audio stack then reports the CAP events listed in Table 4.1 :
| Events | Description | Header File |
|---|---|---|
| CAP_CCP_INST_ACTIVATED_EVT | Event notified when a telephone bearer instance of the call control profile is activated and associated to an audio stream. | cap_types.h |
| CAP_CCP_INST_DEACTIVATED_EVT | Event notified when a telephone bearer instance of the call control profile is deactivated. | cap_types.h |
| CAP_MCP_INST_ACTIVATED_EVT | Event notified when a media player instance of the media control profile is activated and associated to an audio stream. | cap_types.h |
| CAP_MCP_INST_DEACTIVATED_EVT | Event notified when a media player instance of the media control profile is deactivated. | cap_types.h |
Table 4.1 Content Control events
The CAP Acceptor/Commander can performCall control operation and Media control operation on active CCP instance or MCP instance using the functions declared in ccp.h and mcp.h header files.
5. References