This page contains information related to Bluetooth® Low Energy and regional (CE, FCC) certification.
It is assumed that the reader is familiar with STM32WB, STM32WB and/or STM32WBA development. Otherwise, we recommend reading the Introduction to Bluetooth® Low Energy with STM32 guideline first.
1. STMicroelectronics tools for certification
STMicroelectronics provides dedicated STM32WB0/STM32WB/WBA firmware called "Transparent Mode" that can be used for certification purposes.
STMicroelectronics also provides a dedicated GUI PC tool called STM32CubeMonitor-RF[1] that can be used for regional RF certifications.
1.1. Transparent mode firmware
A set of commands and events is sent through the STM32WB/WBA UART or USB to control the Bluetooth® Low Energy stack via the "Transparent Mode" application.
1.1.1. STM32WB0x
For STM32WB0x devices, the "Transparent Mode" firmware is available in the STM32CubeWB0[2] software package. It is available in source code and must be rebuilt using the customer hardware configuration (UART interface used, SMPS used or not, etc.).
For the specific case of STM32WB05xN network coprocessor, a dedicated "Virtual COM Port" firmware is available in the X-CUBE-WB05N[3] software package. It is available in source code for STM32U5 (default) and must be rebuilt according to host microcontroller used and customer hardware configuration (UART interface used etc.).
1.1.2. STM32WB1x, STM32WB3x, STM32WB5x
STM32WB devices embed Arm Cortex®-M4 and Arm Cortex®-M0 network coprocessors.
STM32WB-M0 devices embed the Bluetooth® smart protocol stack. For STM32WB-M4 devices, dedicated "Transparent Mode" firmware is available in the STM32CubeWB[4] software package. It is available in source code and must be rebuilt using the customer hardware configuration (UART interface used, SMPS used or not, etc.).
For firmware examples, refer to:
- The P-NUCLEO-WB55 Nucleo folder if the UART interface is used.
- The P-NUCLEO-WB55 USBDongle folder if the USB interface is used.
1.1.3. STM32WBA5x
For STM32WBA devices, the "Transparent Mode" firmware is available in the STM32CubeWBA[5] software package. It is available in source code and must be rebuilt using the customer hardware configuration (UART interface used, SMPS used or not, etc.).
Refer to the dedicated STM32WBA Transparent Mode wiki page for more details.
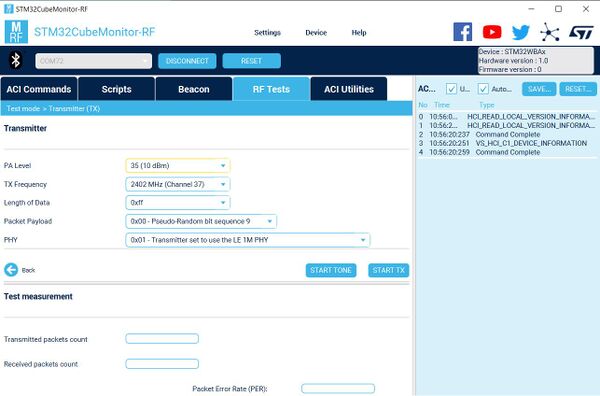
1.2. STM32CubeMonitor-RF PC tool
STM32CubeMonitor-RF[1] is a PC tool for quickly testing the RF performance of STM32WB0/STM32WB/WBA-based hardware devices.
In the RF Tests tab, the required mode (Rx/Tx), modulation, and power settings for the tested device can be configured quickly.
2. Bluetooth® certification
2.1. Bluetooth® Low Energy qualification process
All products using Bluetooth® technology must complete the Bluetooth® qualification process. Please refer to the Bluetooth® SIG webpage (Bluetooth® qualification process overview)[6].
The Bluetooth® qualification process is not a matter of putting the Bluetooth® logo on a product, but of using licensed technology.
2.1.1. Two paths: testing required/no testing required
There are two possible paths for the qualification process:
No testing required
- The product is based on a precertified STMicroelectronics module, such as STM32WB5MMG or STM32WB1MMC.
- The product uses STM32WBx and follows the recommendations outlined in AN5526 for STM32WB0, in AN5165 for STM32WB, in AN5948 for STM32WBA and no changes were made to the schematics and layout.
Testing required
- The product is based on an STMicroelectronics chipset, such as STM32WB0/STM32WB/STM32WBA, and does not follow the recommendations outlined in AN5526 for STM32WB0, in AN5165 for STM32WB, in AN5948 for STM32WBA, and changes were made to the schematics or layout.
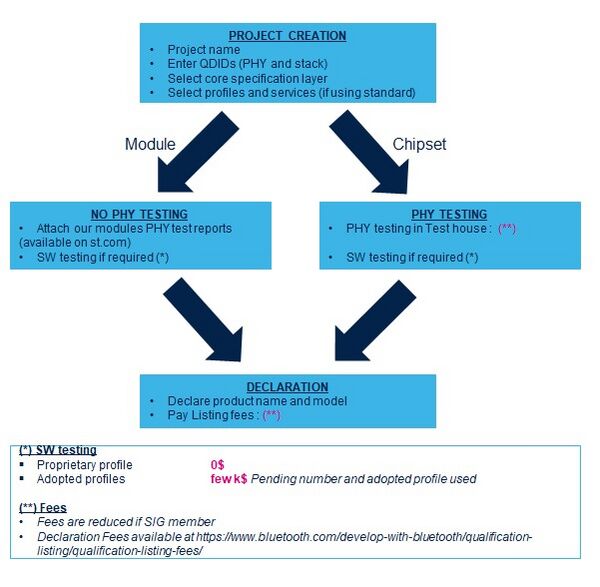
2.1.2. Qualification workspace process flow
The Bluetooth® qualification process example wiki article gives a step-by-step description of the qualification workspace process.
Whatever the STM32WB0, STM32WB or STM32WBA chipset or associated modules used, STMicroelectronics does not provide end product devices, so the required testing path should be used. STMicroelectronics qualified products and provide changes and maintenance to the latest core functionality.
The image below shows the main qualification steps and associated costs:
More information on certification fees is available from the SIG website[7].
The RF-PHY reports for STM32WB modules can be found on st.com:
2.1.3. Bluetooth® qualification test facilities
If testing is required, the qualification testing process takes place in an official Bluetooth® qualification test facility (BQTF). BQTFs are formally recognized by the Bluetooth® SIG as competent to perform Bluetooth® qualification conformance tests.
A list of official BQTFs is available on the Bluetooth® website[10].
2.2. Available qualified design DID/DN (QDID)
The tables below summarize certified Bluetooth® SIG product on RF-PHY, controller-host stack and profiles for all STM32WB0/STM32WB/STM32WBA families.
When proceeding to a new product Bluetooth® SIG certification, customers should determine the corresponding DID/DN (QDID) to the selected STM32WBx hardware and firmware version.
As a reminder:
- It is recommended for customers to start qualification workspace process from latest mandatory TCRL.
- This ensures interoperability between a Bluetooth®v5.1 device and a Bluetooth®v6.0 device, for example.
- All Bluetooth® Low Energy features are optional, so you need to select the necessary features for your application.
2.2.1. STM32WB0 RF-PHY QDID
| Package | Part number | RF PHY QDID |
|---|---|---|
| WLCSP36 QFN32 |
STM32WB05 | 175191 (TCRL 2021-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.3 |
| WLCSP49 QFN32 QFN48 |
STM32WB06 STM32WB07 |
221778 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.4 |
| WLCSP36 QFN32 |
STM32WB09 | 175191 (TCRL 2021-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.3 |
2.2.2. STM32WB0 host stack QDID
| Features | Host stack version | QDID |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 HCI LL with extended advertising, ATT, GAP, GATT, L2CAP with Enhanced Connected Oriented Channel, SMP |
stm32wb0x_ble_stack | 234204 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.4 or
Q334238 Subsystem of Q234204 (without direction finding feature) |
| 4.0 HCI LL with extended advertising |
stm32wb0x_ble_stack_controller_only | 234204 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.4 or
Q334238 Subsystem of Q234204 (without direction finding feature) |
2.2.3. STM32WB RF-PHY DID/DN (&QDID)
| Package | Part number | Cut version | RF-PHY DID/DN (&QDID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| QFN48 | STM32WB55Cx (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbit/s) STM32WB50Cx (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 1 Mbit/s) STM32WB35Cx (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbit/s) STM32WB30Cx (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 1 Mbit/s) |
Y or X | Q308129 (TCRL 2024-2) include QDID 161807 |
| STM32WB15CCU6E (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbit/s) STM32WB10CCU5E (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 1 Mbit/s) |
Y or X | Q308112 (TCRL 2024-2) include QDID 164054 | |
| STM32WB15CXX6 (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbit/s) STM32WB10CXX5 (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 1 Mbit/s) |
Y or X | Q308109 (TCRL 2024-2) include QDID 161969 | |
| QFN68 | STM32WB55Rx (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.0 - 2 Mbit/s) | Y | Q308152 (TCRL 2024-2) include QDID 127495 |
| WLCSP100 | STM32WB55VY (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.3 - 2 Mbit/s) | X | Q306653 (TCRL 2024-2) include QDID 178970 |
| BGA129 | STM32WB55Vxx (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbit/s) | Y or X | Q308129 (TCRL 2024-2) include QDID 161808 |
| WLCSP49 | STM32WB15CCY (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbit/s) STM32WB10CCY (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 1 Mbit/s) |
Y or X | Q307155 (TCRL2024-2) include QDID 170241 |
| Module 86-pin LGA | STM32WB5MMG (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.2 - 2 Mbits/s) | X | Q317109 (TCRL2024-2) include QDID 187035 |
| Module 77-pin LGA | STM32WB1MMC (Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.3 - 2 Mbit/s) | 2.1 | Q306642 (TCRL2024-2) include QDID 187042 |
2.2.4. STM32WB host stack DID/DN (&QDID)
| Features | Host stack version | STM32WB_Copro_Wireless_Binaries | DID/DN (&QDID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LL with extended advertising, 4.0 HCI, ATT, GAP, GATT, SMP, L2CAP with Enhanced Connected Oriented Channel |
STM32CubeFW_WB_BLE_HCI_FULL_EXT STM32CubeFW_WB_BLE_STACK_FULL_EXT |
stm32wb5x_BLE_HCILayer_extended_fw.bin stm32wb3x_BLE_HCILayer_extended_fw.bin stm32wb1x_BLE_HCILayer_extended_fw.bin stm32wb5x_BLE_Stack_full_extended_fw.bin stm32wb3x_BLE_Stack_full_extended_fw.bin stm32wb1x_BLE_Stack_full_extended_fw.bin |
Q309440 (TCRL2024-2) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.4 (include QDID 216169) or Q332452 Subsystem of Q309440 (without Power Class 1 feature) |
Notice that recent DID/DN Q306500 will inherit from all previous QDID software STM32WB_Copro_Wireless_Binaries. As example Q306500 could use variant stm32wb3x_BLE_HCI_AdvScan_fw.bin or stm32wb5x_BLE_Stack_full_fw.bin.
2.2.5. STM32WBA RF-PHY DID/DN
| Package | Part number | Cut version | RF-PHY DID/DN |
|---|---|---|---|
| UFQFPN48 | STM32WBA5xCx | 2.x | Q320738 (TCRL 2024-2) Bluetooth® Low Energy 6.0 |
| WLCSP41 | STM32WBA5xHx | 2.x | |
| UFQFPN32 | STM32WBA5xKx | 2.x | |
| UFBGA59 | STM32WBA5xUx | 2.x | |
| LGA76L (Module) | STM32WBA5Mxx | 2.x | Q349897 (TCRL 2025-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 6.0 |
| UFQFPN48 | STM32WBA6xCx | 1.x | Q336189 (TCRL 2024-2) Bluetooth® Low Energy 6.0 |
| WLCSP88 | STM32WBA6xMx | 1.x | |
| VFQFPN68 | STM32WBA6xRx | 1.x |
2.2.6. STM32WBA host stack DID/DN (&QDID)
| Features | Host stack version | DID/DN (&QDID) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 HCI LL with extended advertising, ATT, GAP, GATT, L2CAP with Enhanced Connected Oriented Channel, SMP |
STM32CubeWBAx_BLE_HCI_FW STM32CubeWBAx_BLE_FULL_FW |
234430 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.4
or Q330021 Subsystem of Q234430 (without Power Class 1 feature) |
| 4.0 HCI LL with extended advertising, ATT, GAP, GATT, L2CAP with Enhanced Connected Oriented Channel, SMP |
STM32CubeWBA_BLE_HCI_FW STM32CubeWBA_BLE_FULL_FW |
227877 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.4 |
| 4.0 HCI LL with extended advertising, ATT, GAP, GATT, L2CAP with Enhanced Connected Oriented Channel, SMP |
STM32Cube_WBA_BLE_HCI_STACK STM32Cube_WBA_BLE_FULL_STACK |
198195 (TCRL 2022-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy 5.3 |
2.2.7. STM32WBA Audio Framework QDID
| Features | Release version | QDID |
|---|---|---|
| STM32WBAx_BLE_AUDIO_PBP_TMAP | STM32CubeWBAx V1.3.x | 237184 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy |
| STM32WBAx_BLE_AUDIO_GAF | STM32WBAx_BLE_AUDIO_GAF V1.2 | 237184 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy |
| STM32WBAx_LC3 | STM32WBAx_LC3 v1.4 | 237184 (TCRL 2023-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy |
2.2.8. STM32WBx Profiles & Services DID/DN
| Features | DID/DN |
|---|---|
| STM32WBA & STM32WB & STM32WB0 Series Profiles & Services | Q302342 (TCRL 2024-1) Bluetooth® Low Energy |
2.3. Qualification workspace process
Aside this certification guideline, we do have few wiki pages describing the different steps of the qualification process for various STM32WBx devices.
Refer to:
- STM32WB05KZ Bluetooth® step by step qualification example wiki article for a step by step example using STM32WB05KZ.
- STM32WB55CG Bluetooth® step by step qualification example wiki article for a step by step example using STM32WB55CG.
- STM32WB5MMG Bluetooth® step by step qualification example wiki article for a step by step example using STM32WB5MMG.
- STM32WBA55CG Bluetooth® step by step qualification example wiki article for a step by step example using STM32WBA55CG.
2.4. Bluetooth® Low Energy RF-PHY testing
In case RF-PHY testing is required, the following chapters contain information on how to prepare the customer's hardware and software.
2.4.1. Software & hardware recommendation for Bluetooth® Low Energy RF testing
The customer should prepare their device to ensure that:
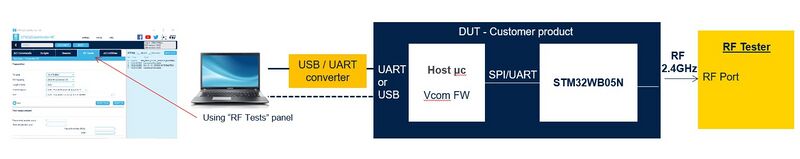
- STM32WB0x, STM32WBx or STM32WBAx is programmed with the "Transparent Mode" firmware.
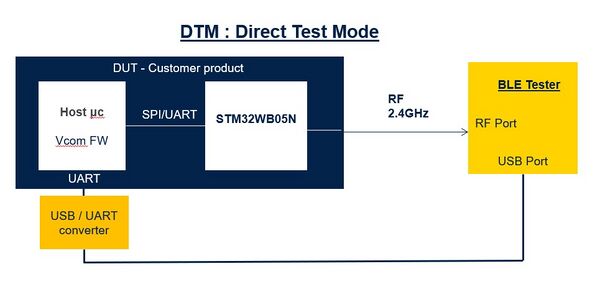
- For STM32WB05xN network coprocessor, host microcontroller is flashed with "Virtual COM Port" firmware.
- The SMA RF cable is set instead of the antenna (to ensure a solid grounding connection), because Bluetooth® Low Energy RF-PHY tests are done in conducted mode only.
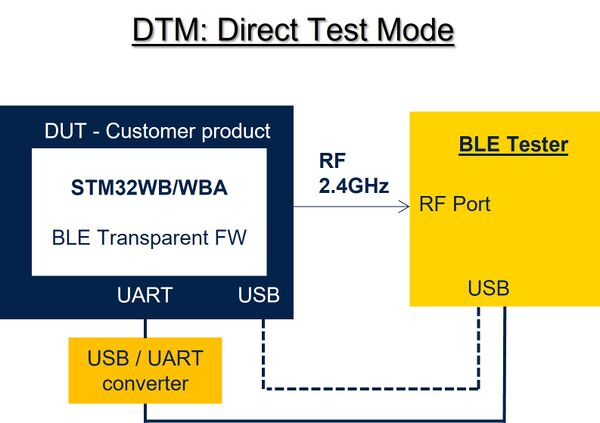
2.4.2. Direct test mode
Direct test mode (where the Bluetooth® tester sends HCI commands directly to the tested device) is mandatory for the Bluetooth® Low Energy qualification, which is why the customer product must be programmed with the "Transparent Mode" firmware (refer to the chapter on "Transparent Mode" firmware above).
For the specific case of network coprocessor with STM32WB05xN, please refer to below picture.
2.4.3. Protocol implementation extra information for testing (Pixit)
The protocol implementation extra information for testing contains additional information necessary for testing. When proceeding to the RF PHY tests, the customer might need to provide the test house with this information about the chipset RF PHY.
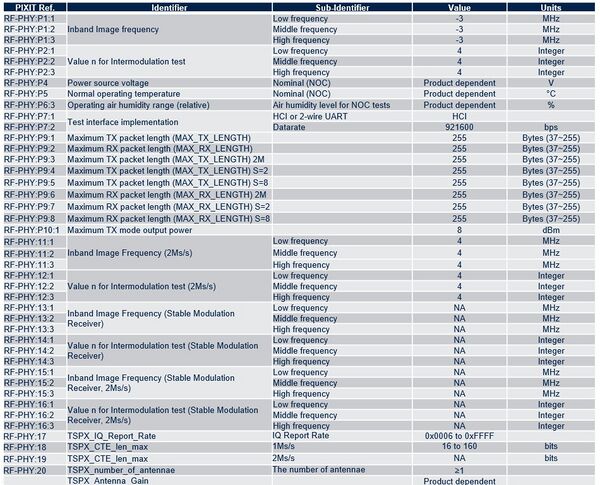
2.4.3.1. STM32WB0
The table below lists the information needed for STM32WB0 devices:
Note 1: some information is product-related and not chipset-related (noted “Product dependent” in the table).
Note 2: If some features are not used (2M, AoA/AoD corresponding details should be set to “NA”.
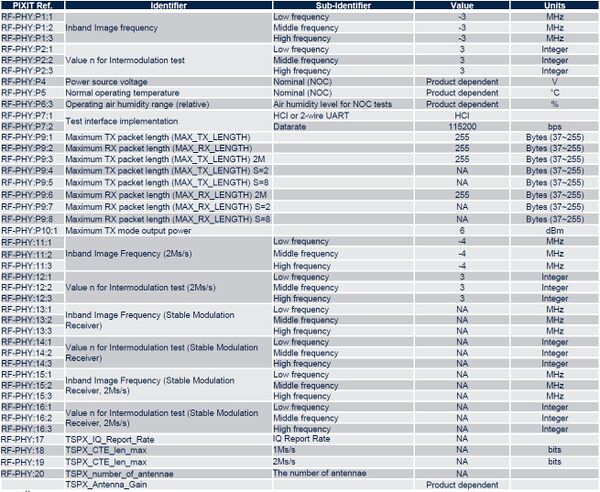
2.4.3.2. STM32WB
The table below lists the information needed for STM32WB devices:
Note 1: some information is product-related and not chipset-related (noted “Product dependent” in the table).
Note 2: 2M tests should be set to “NA” if the device does not support 2M modulation.
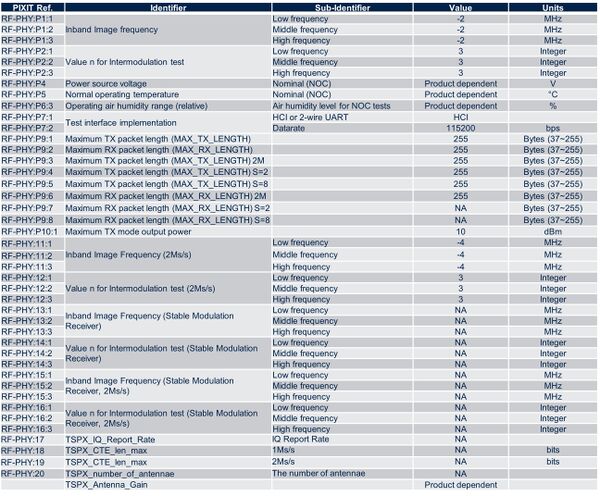
2.4.3.3. STM32WBA
The table below lists the information needed for STM32WBA devices:
Note 1: some information is product-related and not chipset-related (noted “Product dependent” in the table).
Note 2: 2M tests should be set to “NA” if the device does not support 2M modulation.
3. Regional certification
Bluetooth® Low Energy products need to comply with different regional RF regulatory requirements in different countries, such as:
- FCC (Federal Communications Committee) for North America.
- European Commission Radio Equipment Directive (RED) for Europe.
- IC (Industry Canada) for Canada, etc.
3.1. Module versus chipset
3.1.1. Chipset use case
STM32WB0/STM32WB/STM32WBA chipsets are compliant with all regional RF regulatory requirements. However, RF tests for regional certifications are fully hardware-dependent (antenna, layout, etc.).
3.1.2. Module use case
STM32WBxMMx modules have been precertified for RF in various regions. Certificates and test reports for STM32WB1M[11] and STM32WB5M[12] are available on our website.
Only a limited number of RF tests is required for the final product (Rx and Tx radiated tests) when using our certified modules, which reduces the RF test costs for the end product significantly.
3.2. Regional certification testing
3.2.1. Setup for RF testing
The customer must prepare their DUT to ensure that:
- STM32WB is programmed with the "Transparent Mode" firmware.
- The tested device is connected to the STM32CubeMonitor-RF[1] PC tool.
- The RF test is done in conducted and mainly radiated mode. For conducted tests, the RF cable should be implemented, replacing the antenna (to ensure a solid grounding connection).
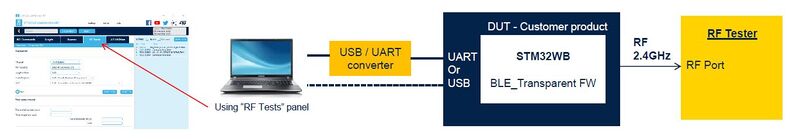
The picture below describes the recommended test setup for performing RF tests for regional certification.
For the specific case of STM32WB05xN network coprocessor
- Host microcontroller is programmed with the "Virtual Com Port" firmware.
- The tested device is connected to the STM32CubeMonitor-RF[1] PC tool.
- The RF test is done in conducted and mainly radiated mode. For conducted tests, the RF cable should be implemented, replacing the antenna (to ensure a solid grounding connection).
The picture below describes the recommended test setup for performing RF tests for regional certification.
3.2.2. RED - EN 300 328 prefilled document
Customers are asked to fill out an EN 300 328 form for RED RF testing. The images below show a prefilled form with the suggested values related to STM32WB/WBA (to be completed with product-related information).
3.2.3. Immunity tests
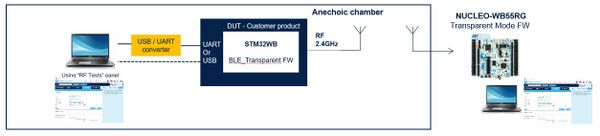
For regional certification, the test house checks whether the final product is able to sustain Bluetooth® Low Energy communication when subject to EMC stress. A possible test setup is detailed below:
- The tested device has been programmed with the "Transparent Mode" firmware and is connected to STM32CubeMonitor-RF.
- The STM32WB evaluation kit (for example) is also used outside the anechoic chamber. It has been programmed with the "Transparent Mode" firmware and is also connected to STM32CubeMonitor-RF.
- The ACI Utilities tab in STM32CubeMonitor-RF lets you quickly establish a Bluetooth® Low Energy link between the DUT and an STMicroelectronics evaluation kit. You can then check any disconnections during the EMC stress test.
- DUT advertises:
- STM32WB scans:
- STM32WB connects:
- If the RF link with the DUT is broken, the disconnection is displayed:
4. References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 STM32CubeMonitor-RF
- ↑ STM32CubeWB0 software package
- ↑ X-CUBE-WB05N expansion software package
- ↑ STM32CubeWB software package
- ↑ STM32CubeWBA software package
- ↑ Bluetooth® Qualification Process Overview
- ↑ Bluetooth® SIG website
- ↑ STM32WB5MMG (cutX) RF PHY test report
- ↑ STM32WB1MMC (cutX) RF PHY test report
- ↑ Bluetooth® qualification test facilities
- ↑ STM32WB5M RF test report
- ↑ STM32WB1M RF test report