1. Article purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to
- briefly introduce the QUADSPI peripheral and its main features
- indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block
- explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components
- explain, when needed, how to configure the QUADSPI peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit source]
The Quad-SPI interface (QUADSPI peripheral) interfaces the processor with serial NOR flash and serial NAND flash memories.
It supports:
- Single, Dual- or Quad-SPI flash memories
- A dual-flash mode, allowing to aggregate two flash memories into a virtual-single one
- Dual data rate and memory-mapped modes.
2.1. Features[edit source]
Refer to STM32MP13 reference manuals or STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete feature list and to the software components introduced below to know the implemented features.
2.2. Security support[edit source]
2.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
The QUADSPI is a secure peripheral (under ETZPC control).
2.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
The QUADSPI is a non-secure peripheral.
3. Using the peripheral-associated software[edit source]
3.1. Boot time[edit source]
QUADSPI instance is a boot device that supports serial boot for flash programming with STM32CubeProgrammer.
3.2. Runtime[edit source]
3.2.1. Overview[edit source]
Allocation of the QUADSPI instances can be:
- The Arm® Cortex®-A7 secure context, on STM32MP13x lines
 only, but this is not supported in OpenSTLinux.
only, but this is not supported in OpenSTLinux.
or
- The Arm® Cortex®-A7 non-secure core to be controlled in Linux® by the MTD framework
or
- The Arm® Cortex®-M4, on STM32MP15x lines
 only, to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by QUADSPI HAL driver
only, to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by QUADSPI HAL driver
Chapter #Peripherals assignment describes which peripheral instances can be assigned to which context.
3.2.2. Software frameworks[edit source]
3.2.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | |||
| Mass storage | QUADSPI | Linux MTD framework | ||
3.2.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | STM32Cube | |||
| Mass storage | QUADSPI | Linux MTD framework | STM32Cube QUADSPI driver | ||
3.2.3. Peripheral configuration[edit source]
The firmware, running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned, applies the configuration that can be done alone via the STM32CubeMX tool for all internal peripherals and then manually completed (particularly for external peripherals), according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article.
For Linux kernel configuration, please refer to QUADSPI device tree configuration.
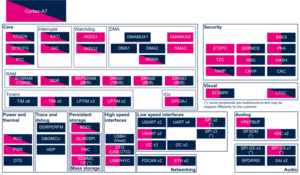
3.2.4. Peripherals assignment[edit source]
3.2.4.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) | |||
| Mass storage | QUADSPI | QUADSPI | ⬚ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) |
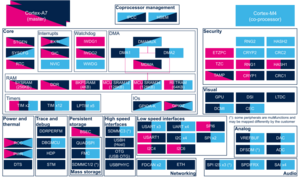
3.2.4.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Mass storage | QUADSPI | QUADSPI | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |
4. References[edit source]