1. Peripheral overview[edit source]
The DTS peripheral is used to monitor the device temperature and take some preventive action (like frequency scaling or peripheral disabling) in case it is becoming too high and before destroying the component.
1.1. Features[edit source]
Refer to the STM32MP13 reference manuals or STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features , and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
1.2. Security support[edit source]
The DTS is a non secure peripheral.
2. Peripheral usage and associated software[edit source]
2.1. Boot time[edit source]
DTS is not used at boot time.
2.2. Runtime[edit source]
2.2.1. Overview[edit source]
The monitoring is done from the Cortex-A7 non-secure context with Linux® thermal management framework.
2.2.2. Software frameworks[edit source]
2.2.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | |||
| Power & Thermal | DTS | Linux thermal framework | ||
2.2.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | STM32Cube | |||
| Power & Thermal | DTS | Linux thermal framework | |||
2.2.3. Peripheral configuration[edit source]
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned. The configuration can be done alone via the STM32CubeMX tool for all internal peripherals, and then manually completed (particularly for external peripherals), according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article.
2.2.4. Peripheral assignment[edit source]
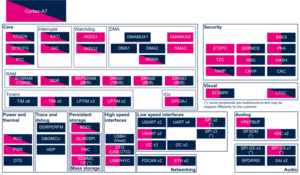
2.2.4.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) | |||
| Power & Thermal | DTS | DTS | ☐ | ||
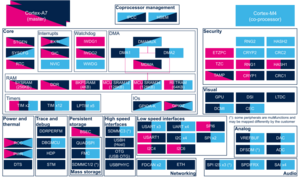
2.2.4.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Power & Thermal | DTS | DTS | ☐ | |||
3. References[edit source]