deleted>Frq08988 mNo edit summary |
Registered User mNo edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude>{{ApplicableFor | ||
{{ | |MPUs list=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x | ||
|MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x | |||
}}</noinclude> | |||
</noinclude> | |||
==Article purpose== | ==Article purpose== | ||
The purpose of this article is to: | The purpose of this article is to: | ||
* briefly introduce the FDCAN peripheral and its main features | * briefly introduce the FDCAN peripheral and its main features | ||
* indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block | * indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block | ||
* explain how each instance can be allocated to the | * explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components | ||
* explain, when necessary, how to configure the FDCAN peripheral. | * explain, when necessary, how to configure the FDCAN peripheral. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 20: | ||
FDCAN1 and FDCAN2 share a dedicated 10 Kbyte CAN SRAM for message transfers.<br /> | FDCAN1 and FDCAN2 share a dedicated 10 Kbyte CAN SRAM for message transfers.<br /> | ||
Refer to [[STM32MP15 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP15 reference manuals]] for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.<br> | Refer to [[STM32MP13 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP13 reference manuals]] or [[STM32MP15 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP15 reference manuals]] for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.<br> | ||
===Security support=== | ===Security support=== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 32: | ||
====Overview==== | ====Overview==== | ||
FDCAN instances can be allocated to: | FDCAN instances can be allocated to: | ||
* the Arm | * the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A7 non-secure core to be controlled in Linux<sup>®</sup> by the NetDev framework (See [[CAN overview]]) | ||
or | or, on {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}} only | ||
* the Arm | * the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M4 to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by [[STM32CubeMP1 architecture|STM32Cube FDCAN driver]] | ||
====Software frameworks==== | ====Software frameworks==== | ||
{{: | ===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=13}} ===== | ||
{{:STM32MP13 internal peripherals software table template}} | |||
| Networking | |||
| [[FDCAN internal peripheral|FDCAN]] | |||
| | |||
| Linux net/can framework | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}} ===== | |||
{{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_software_table_template}} | |||
| Networking | | Networking | ||
| [[FDCAN internal peripheral|FDCAN]] | | [[FDCAN internal peripheral|FDCAN]] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 59: | ||
====Peripheral configuration==== | ====Peripheral configuration==== | ||
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned. The configuration can be done alone via the [[STM32CubeMX]] tool for all internal peripherals, and then manually completed (particularly for external peripherals) according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article. | The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned. The configuration can be done alone via the [[STM32CubeMX]] tool for all internal peripherals, and then manually completed (particularly for external peripherals) according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article. | ||
When the FDCAN peripheral is assigned to the Linux | When the FDCAN peripheral is assigned to the Linux<sup>®</sup> OS, it is configured through the device tree according to the information given in the [[FDCAN device tree configuration]] article. | ||
====Peripheral assignment==== | ====Peripheral assignment==== | ||
{{: | ===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=13}} ===== | ||
< | {{:STM32MP13_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template}} | ||
<section begin=stm32mp13 /> | |||
| rowspan="2" | Networking | |||
| rowspan="2" | [[FDCAN internal peripheral|FDCAN]] | |||
| FDCAN1 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| FDCAN2 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp13 /> | |||
|} | |||
===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}} ===== | |||
{{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp15 /> | |||
| rowspan="2" | Networking | | rowspan="2" | Networking | ||
| rowspan="2" | [[FDCAN internal peripheral|FDCAN]] | | rowspan="2" | [[FDCAN internal peripheral|FDCAN]] | ||
| Line 71: | Line 96: | ||
| Assignment (single choice) | | Assignment (single choice) | ||
|- | |- | ||
</ | <section end=stm32mp15 /> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
<noinclude> | |||
{{ArticleBasedOnModel | Internal peripheral article model}} | |||
{{PublicationRequestId | 9882 | 2018-12-04 | BrunoB}} | |||
[[Category:Networking peripherals]] | |||
</noinclude> | |||
Latest revision as of 15:40, 1 February 2022
1. Article purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the FDCAN peripheral and its main features
- indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block
- explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components
- explain, when necessary, how to configure the FDCAN peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit source]
FDCAN peripheral handles data communication in a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus system using message-based protocol originally designed for in-vehicle communication.
The CAN subsystem consists of two CAN modules (FDCAN1 and FDCAN2), a shared message RAM and an optional clock calibration unit.
2.1. Features[edit source]
Both FDCAN instances are compliant with classic CAN protocol[1] and CAN FD[2] (CAN with Flexible Data-Rate) protocol.
In addition, FDCAN1 supports time triggered CAN (TTCAN).
FDCAN1 and FDCAN2 share a dedicated 10 Kbyte CAN SRAM for message transfers.
Refer to STM32MP13 reference manuals or STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
2.2. Security support[edit source]
FDCAN is a non secure peripheral.
3. Peripheral usage and associated software[edit source]
3.1. Boot time[edit source]
The FDCAN is not used at boot time.
3.2. Runtime[edit source]
3.2.1. Overview[edit source]
FDCAN instances can be allocated to:
- the Arm® Cortex®-A7 non-secure core to be controlled in Linux® by the NetDev framework (See CAN overview)
- the Arm® Cortex®-M4 to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by STM32Cube FDCAN driver
3.2.2. Software frameworks[edit source]
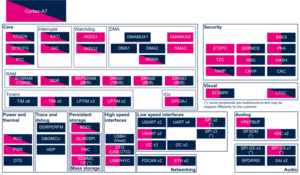
3.2.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | |||
| Networking | FDCAN | Linux net/can framework | ||
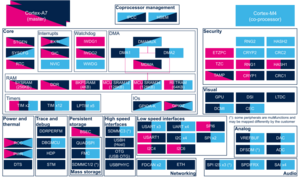
3.2.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | STM32Cube | |||
| Networking | FDCAN | Linux net/can framework | STM32Cube FDCAN driver | ||
3.2.3. Peripheral configuration[edit source]
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned. The configuration can be done alone via the STM32CubeMX tool for all internal peripherals, and then manually completed (particularly for external peripherals) according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article. When the FDCAN peripheral is assigned to the Linux® OS, it is configured through the device tree according to the information given in the FDCAN device tree configuration article.
3.2.4. Peripheral assignment[edit source]
3.2.4.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) | |||
| Networking | FDCAN | FDCAN1 | ☐ | ||
| FDCAN2 | ☐ | ||||
3.2.4.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Networking | FDCAN | FDCAN1 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |
| FDCAN2 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |||
4. References[edit source]
- ↑ CAN protocol implementations, from the CAN in Automation group (CiA)
- ↑ CAN FD - The basic idea, from the CAN in Automation group (CiA)