Registered User (Merge articles) |
Registered User mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
====Peripheral assignment==== | ====Peripheral assignment==== | ||
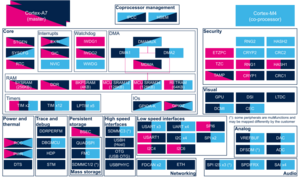
{{: | {{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template}} | ||
<onlyinclude> | <onlyinclude> | ||
| rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | | rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 1 February 2022
1. Article purpose
The purpose of this article is to:
- Briefly introduce the TSGEN peripheral and its main features
- Indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block
- Explain how each instance can be allocated to the three runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components
- Explain, when necessary, how to configure the TSGEN peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview
The TSGEN peripheral generates a universal reference in time, named timestamps, and sends it to the CoreSight™ source peripherals (such as STM and ETM internal peripherals). Source peripherals use then this reference to integrate it in the generated trace. Since multiple trace generators can be implemented in a CoreSight system, the timestamp allows traces to be ordered chronologically.
2.1. Features
Refer to the STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are really implemented.
2.2. Security support
The TSGEN is a non secure peripheral.
3. Peripheral usage and associated software
3.1. Boot time
The TSGEN can be used at boot time to provide time stamping for ETM and STM traces.
3.2. Runtime
3.2.1. Overview
The TSGEN can be used at run time to provide time stamping for ETM and STM traces.
3.2.2. Software frameworks
There is no software dedicated to the TSGEN internal peripheral delivered with STM32MPU ecosystem.
3.2.3. Peripheral configuration
Configuration of the TSGEN is done via JTAG scripts. Those scripts must be built by the user thanks to STM32MP15 reference manuals .
3.2.4. Peripheral assignment
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Trace & Debug | TSGEN | TSGEN | No assignment possible | |||
4. References