1. Article purpose[edit source]
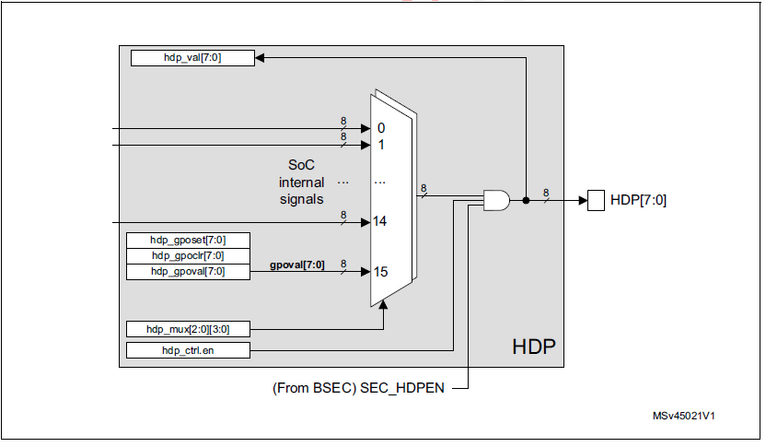
This article introduces the Hardware Debug Port which allows the observation of internal signals. By using multiplexers, up to 16 signals of each of 8-bit output can be observed. The article explains:
- How to configure, use and debug the driver
- The driver structure, and where the source code can be found.
2. Short description[edit source]
- 8 output signals
- One of 16 internal signals with individual control
- 8 software-programmable signals for pinout agnostic code debugging
- Output disabling by security signal
3. Configuration[edit source]
3.1. Kernel configuration[edit source]
The HDP is enabled and ready to be used in all STM32MPU Embedded Software Distributions, via the Linux® kernel configuration CONFIG_STM32_HDP, set to disabled by default.
Symbol: STM32_HDP Location: Device Drivers [*] SOC (System On Chip) specific Drivers [*] STMicroelectronics STM32MP157 Hardware Debug Port (HDP) pin control
Please refer to the Menuconfig or how to configure kernel article for instructions on modifying the configuration, and recompiling the Linux kernel image in the Distribution Package context.
3.2. Device tree[edit source]
Refer to the HDP device tree configuration article when configuring the HDP Linux kernel driver.
4. How to trace and debug[edit source]
4.1. How to monitor[edit source]
4.1.1. How to monitor with debugfs[edit source]
sysfs entry can be used to browse HDP registers.
/sys/kernel/debug/hdp# ls
ctrl gpoclr gposet gpoval mux val
See the HDP chapter in the reference manual [1] for further register details.
5. Source code location[edit source]
The HDP Linux driver source code is composed of:
- “<Linux kernel directory>/drivers/soc/st/stm32_hdp.c” to handle common resources: registers, clock.
6. References[edit source]