| Coming soon |
This article explains what is DMA and how to use it through examples
1. What is DMA?
DMA stands for Direct Memory Access controller. It is a bus master and system peripheral.
The DMA is is used in order to provide high-speed data transfer between peripherals and memory as well as memory to memory. Data can be quickly moved by DMA without any CPU actions. This keeps CPU resources free for other operations.
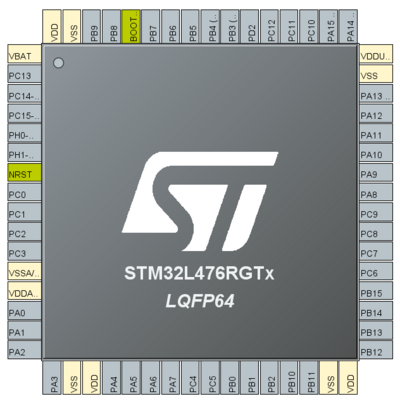
During this article, we will be using the STM32L476 Nucleo board.
This device embeds 2 DMAs: DMA1 and DMA2.
Each channel is dedicated to managing memory access requests from one or more peripherals.
The two DMA controllers have 14 channels in total, each dedicated to managing memory access requests from one or more peripherals. Each has an arbiter for handling the priority between DMA requests.
| DMA features | DMA1 | DMA2 |
| Number of regular channels | 7 | 7 |
1.1. Objective
- Learn how to setup DMA transfer in STM32CubeIDE
- Create simple DMA memory to memory transfer from RAM to RAM, Peripheral to RAM and transfer with Interrupt
1.2. How to
- Use CubeIDE and Generate Code with DMA
- Learn how to setup the DMA in HAL
- Verify the correct functionality by comparing transferred buffers
2. Create the project in STM32CubeIde
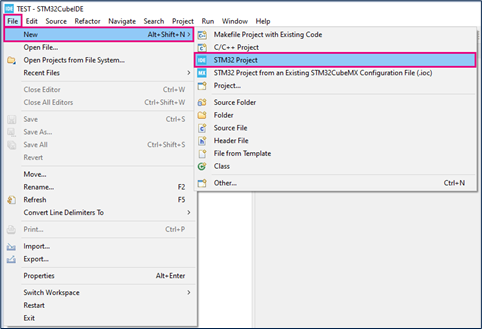
'File > New > STM32 Project in main panel.
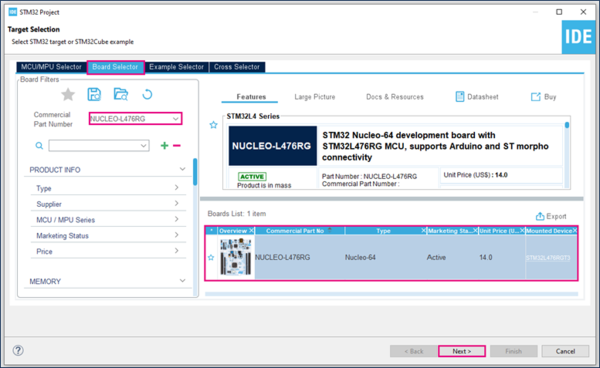
This example uses the NUCLEO-L476RG board.
Start by selecting the NUCLEO-L476RG board using the Board Selector as shown in the figure below:
In case you haven't downloaded the STM32L476 Cube library, it will be downloaded automatically. This however may take some time.
Save the project.
- For DMA we don’t need to configure any pins
3. Peripheral to Peripheral Mode
Any DMA channel can operate in peripheral-to-peripheral mode:
- when the hardware request from a peripheral is selected to trigger the DMA channel, this peripheral is the DMA initiator and paces the data transfer from/to this peripheral to/from a register belonging to another memory-mapped peripheral (this one being not configured in DMA mode).
- when no peripheral request is selected and connected to the DMA channel, the software configures a register-to-register transfer by setting the MEM2MEM bit of the DMA_CCRx register.
4. Memory to Memory Mode
The DMA channels may operate without being triggered by a request from a peripheral. This mode is called memory-to-memory mode, and is initiated by software.
Memory to Memory mode allows transfer from one address location to another without a hardware request.
Once the channel is configured and enabled, the transfer starts immediately.
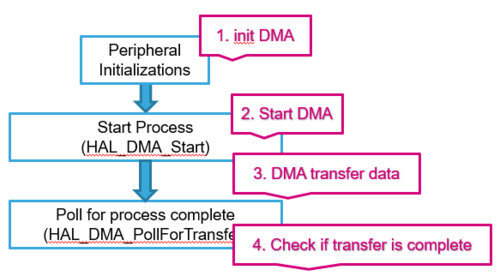
4.1. DMA process workflow summary
At the beginning of the main program the HAL_Init() function is called to reset all the peripherals, initialize the Flash interface and the systick.
Using HAL_DMA_Start() to start DMA transfer after the configuration of Source address and destination address and the Length of data to be transferred.
Using HAL_DMA_PollForTransfer() to poll for the end of current transfer, in this case a fixed Timeout can be configured by User depending from his application.
At the end of the transfer, it is recommended to handle the return values to be sure that program working as expected
- HAL_OK : DMA transfer was successfully finished and data was transferred to destination without error.
- HAL_ERROR : Error occurs during DMA transfer you use HAL_DMA_GetError for details what happened.
- HAL_BUSY : DMA transfer in progress, user can only abort the transfer
4.2. DMA M2M Configuration
In order to run on maximum frequency, setup clock system
Accéder à Pinout & Configuration > DMA >DMA1 Button Add.
Select
- MEMTOMEM DMA request : DMA1 Channel 1
- Normal mode
- Increment source and destination address
- Byte data width
- Generate the code by pressing Ctrl + S :
- Open main.c in Project Explorer / myproject / Src / main.c.
- Create two buffers : one foe the source data and the second as destination buffer
- Insert the following lines between /* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */ and /* USER CODE END 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint8_t Buffer_Src[]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
uint8_t Buffer_Dest[10];
/* USER CODE END 0 */
- Now Insert the following lines between /* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */ and /* USER CODE END 2 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_DMA_Start(&hdma_memtomem_dma1_channel1, (uint32_t) (Buffer_Src), (uint32_t) (Buffer_Dest), 10);
while(HAL_DMA_PollForTransfer(&hdma_memtomem_dma1_channel1, HAL_DMA_FULL_TRANSFER, 100) != HAL_OK)
{
__NOP();
}
/* USER CODE END 2 */
5. Circular Mode
The circular mode is in memory-to-peripheral or peripheral-to-memory transfers.
6. Data Transfer over DMA with Interrupt
[[category:Getting_started_with_STM32_system_peripherals | 30]]